This week’s Pandora Report covers updates from the Biodefense Graduate Program, the Risky Research Review Act, H5N1 updates, the UNGA’s adoption of the Pact for the Future, and more.
Schar School Virtual Information Sessions
If you are interested in a career in biodefense or global health security or want to develop the knowledge and skills necessary to work at the nexus of health, science, and security, find out what the Schar School of Policy and Government has to offer. A virtual open house for all of the Schar School’s master’s and certificate programs will be held online on Monday, September 30, 7-8 PM ET. The Schar School offers flexible part-time or full-time options for graduate certificate and master’s degree programs that teach applicable, real-world skills for in-demand careers. Register here.
Talking Global BioLabs in Galveston
Dr. Gregory Koblentz, Director of the Biodefense Graduate Program, was in Galveston, Texas this week to give a talk as part of the Biosafety and Bioethics Seminar series sponsored by the Institute for Human Infections and Immunity, the Institute for Translational Sciences, and the Department of Bioethics and Health Humanities at the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB). Dr. Koblentz’s talk, “The Global BioLabs Initiative and Biorisk Management,” provided an overview of the results of the Global BioLabs 2023 report and its recommendations for strengthening global biorisk management. While in Galveston, Dr. Koblentz was given a guided tour of the Galveston National Laboratory, one of two BSL-4 labs at UTMB. For biosafety and biosecurity reasons, he was not allowed into the lab space, but he enjoyed visiting the HVAC floors which are marvels of mechanical engineering. In addition, Dr. Koblentz visited the positive pressure suit storage area where he learned that Dover, the sole US-based manufacturer of positive pressure suits, is no longer producing these suits. Dr. Koblentz also had the opportunity to visit the Biocontainment Care Unit (BCU) operated by the Special Pathogens Excellence in Clinical Treatment, Readiness, and Education (SPECTRE) Program at UTMB. The BCU is a 6-room critical care unit that can manage patients infected with highly infectious diseases such as Ebola. Luckily, the BCU has not had to treat such a patient, but it stays busy by providing training, education and research to benefit other healthcare facilities in HHS/FEMA Region VI.
Risky Research Review Act 2.0
On September 25, the Senate Homeland Security and Government Affairs Committee voted 8-1 to approve an amended version of the Risky Research Review Act introduced by Senator Rand Paul (R-KY), ranking member of the committee. According to Senator Paul, the “bipartisan Risky Research Review Act, a first-of-its-kind proposal to establish a Life Sciences Research Security Board within the Executive Branch…The Life Sciences Research Security Board will serve as an independent body responsible for thoroughly evaluating gain-of-function research and other potentially harmful studies involving high-consequence pathogens.” The text of the bill can be found here. In July, Biodefense program director Gregory Koblentz co-authored an opinion piece with David Gillum and Rebecca Moritz that identified significant problems with original version of the bill, “While the Risky Research Review Act aims to address legitimate concerns about the potential hazards associated with life sciences research, its current form is deeply flawed, posing significant threats to scientific progress and public safety. The broad and ambiguous definition of high-risk research, the overreach in funding decisions, and the inadequacies in the board’s composition all point to a need for a more thoughtful and effective approach.” It remains to be seen whether the amended version satisfactorily addresses the deficiencies in the original bill.
UN Adopts Pact for the Future
World leaders gathered in New York for the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Pact for the Future last week. In a press release, the UN described the pact as “… the culmination of an inclusive, years-long process to adapt international cooperation to the realities of today and the challenges of tomorrow. The most wide-ranging international agreement in many years, covering entirely new areas as well as issues on which agreement has not been possible in decades, the Pact aims above all to ensure that international institutions can deliver in the face of a world that has changed dramatically since they were created.”
The pact promises to refocus on existing obligations and commitments to nuclear and biological disarmament, aiming to make relevant global institutions more representative and responsive in the process. Action 26 in the document specifically focuses on disarmament obligations and commitments. It reads:
47. We express our serious concern at the increasing number of actions that are contrary to existing international norms and non-compliance with obligations in the field of disarmament, arms control and non-proliferation. We will respect international law that applies to weapons, means and methods of warfare, and support progressive efforts to effectively eradicate the illicit trade in arms. We recognize the importance of maintaining and strengthening the role of the United Nations disarmament machinery. Any use of chemical and biological weapons by anyone, anywhere and under any circumstances is unacceptable. We call for full compliance with and implementation of relevant treaties. We reaffirm our shared determination to exclude completely the possibility of biological agents and toxins being used as weapons and to strengthen the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. We decide to:
(a) Revitalize the role of the United Nations in the field of disarmament, including by recommending that the General Assembly pursue work that could support preparation of a fourth special session devoted to disarmament (SSOD-IV);
(b) Pursue a world free from chemical and biological weapons and ensure that those responsible for any use of these weapons are identified and held accountable;
(c) Address emerging and evolving biological risks through improving processes to anticipate, prevent, coordinate and prepare for such risks, whether caused by natural, accidental or deliberate release of biological agents;
(d) Identify, examine and develop effective measures, including possible legally binding measures, to strengthen and institutionalize international norms and instruments against the development, production, acquisition, transfer, stockpiling, retention and use of biological agents and toxins as weapons;
(e) Strengthen measures to prevent the acquisition of weapons of mass destruction by non-State actors;
(f) Redouble our efforts to implement our respective obligations under relevant international instruments to prohibit or restrict conventional weapons due to their humanitarian impact and take steps to promote all relevant aspects of mine action;
(g) Strengthen our national and international efforts to combat, prevent and eradicate the illicit trade in small arms and light weapons in all its aspects;
(h) Address existing gaps in through-life conventional ammunition management to reduce the dual risks of unplanned conventional ammunition explosions and the diversion and illicit trafficking of conventional ammunition to unauthorized recipients, including to criminals, organized criminal groups and terrorists.
H5N1 Updates
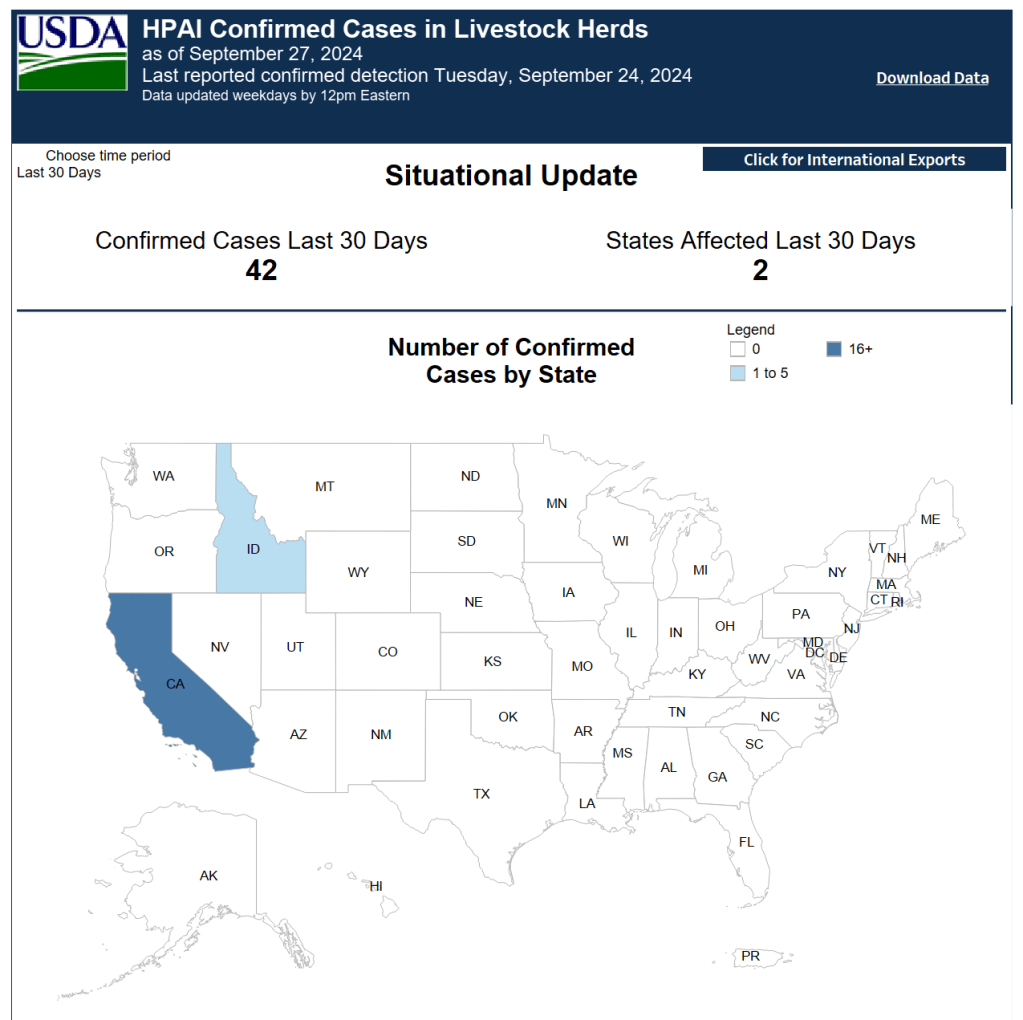
Missouri Healthcare Workers Who Cared for H5N1 Patient Not Tested After Developing Respiratory Symptoms
Last Friday, the CDC reported that a second healthcare worker who cared for a patient hospitalized in Missouri with H5N1 avian influenza developed respiratory symptoms. The patient and a household contact who also became ill have both recovered. Through contact investigation, the state discovered that healthcare workers who cared for the patient developed mild respiratory symptoms. The first worker’s symptoms resolved before the investigation began. State health officials told the CDC they did not learn of the second worker’s symptoms until after they had recovered, making it too late for diagnostic testing. CDC says that serologic testing will be offered to this worker.
Concerns About Lack of Testing Grow as California Reports More Outbreaks
Questions and concerns about the true extent of the H5N1 outbreak in the US are growing, with California reporting eighteen more outbreaks concentrated in herds in its Central Valley this week. Experts worry a lack of testing in both humans and animals is helping conceal the true extent of the outbreak across the nation. In addition to the Missouri healthcare workers, 663 poultry workers in Colorado are known to have been exposed. Of those, 109 reported symptoms and consented to testing, with nine testing positive in July.
Farms near the affected herds in California will begin bulk milk testing. Colorado mandated bulk milk testing, which promptly led to the discovery of outbreaks in an additional eleven herds. Eric Deeble, Deputy Undersecretary for Marketing and regulatory Programs at the USDA, said in a call in August that officials have considered requiring such testing through mandates, but had opted not to. He also said that the success in Colorado is “probably unique to Colorado, and extrapolating out to the rest of the country is not entirely appropriate.”
Currently, the USDA requires H5N1 testing only for dairy cows who are lactating and will be moved across state lines. Deeble expressed a high degree of confidence that the current level of testing is accurately capturing cases in animals being moved between states. He did also say “I do feel like the response is adequate,” in regards to spread and movement within states, even though it is not being monitored as closely.
Efforts to Control Mammal-to-Mammal Transmission Aren’t Working
Researchers led by the UK’s Pirbright Institute recently published an article in Nature that offers an overview of the current H5N1 avian influenza panzootic in mammals. The article-“The Global H5N1 Influenza Panzootic in Mammals”-includes analysis of H5N1 outbreaks European fur farm animals, South American marine mammals, and US dairy cattle. It notes the diversity of these outbreaks and that the virus is at increased risk for spillover to different mammals because of changes to its ecology and molecular evolution in birds.
Read CIDRAP’s Lisa Schnirring’s discussion of the article and its implications here.
US Announces More Mpox Vaccine Donations
This week, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR), announced it is undertaking actions to help increase the United States’ supply of mpox vaccine and support the nation’s commitment to make more than a million doses available to the global mpox response. These actions include:
- “The United States is donating 1,000,000 doses to the international mpox response. The United States has also committed to provide at least $500 million to support the mpox response, aligned with the WHO and Africa CDC Joint Response Plan.”
- “ASPR is also loaning JYNNEOS manufacturer Bavarian Nordic 200,000 doses of ASPR-procured vaccine to ensure continued supply within the domestic commercial market. This action allows uninterrupted access to Americans without diminishing the manufacturer’s availability to fulfill international orders and donations.”
- “ASPR is collaborating with the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) to make JYNNEOS that may otherwise expire available to HRSA funded health centers and Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program Part C and D clinics. These doses are available from the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS) for the purposes of expanding vaccine access for at-risk uninsured and underinsured individuals who otherwise cannot afford them.”
- “These latest vaccine donation announcements follow a USG donation of 50,000 doses of mpox vaccine that was delivered to the DRC on September 10.”
- “Another 10,000 doses of USG donated mpox vaccine were delivered to Nigeria in August 2024 to support the government’s clade I mpox response.”
- “These vaccine efforts build off the $1.94 billion ASPR has invested in funds and technical expertise to develop and sustain JYNNEOS. The product would not exist without the investment and technical expertise provided by the USG.”
- “Other HHS actions include case surveillance, risk communication and community engagement, laboratory supplies and diagnostics, infection prevention and control, increasing capacity for local field epidemiologists, and vaccine planning.”
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra said in a statement, “A public health threat to one is a public health threat to all. HHS is committed to fighting the current mpox outbreak, including through this vaccine donation. Disease doesn’t respect borders and it is our duty to work together to make our world healthier. Our partnerships across the globe in fighting infectious disease will help keep us safe.”
ARPA-H Announces Awards for Developing Multi-Virus Vaccine Design Computational Platform
HHS’ Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) announced this week the teams that will receive awards from the agency’s Antigens Predicted for Broad Viral Efficacy through Computational Experimentation (APECx) program. The announcement explains that “APECx will pursue three technical areas: high-throughput biochemical analysis and protein engineering, protein modeling toolkit development for antigen design, and translational candidate development and clinical evaluation. Antigens and targets identified through these technical areas will then be evaluated for their ability to target entire viral families with a single vaccine.”
The teams are led by:
- La Jolla Institute for Immunology focusing on beta and gamma-herpesvirus antigen and vaccine candidate development, including cytomegalovirus infections.
- University of Washington focusing on alpha and gamma-herpesvirus antigen and vaccine candidate development, including herpes simplex virus infections.
- Vaccine Company, Inc. focusing on vaccine development for flaviviruses, which include threats such as West Nile virus, dengue virus, and Zika virus.
- Vanderbilt University focusing on antigen design and vaccine candidate development against alphaviruses, such as Chikungunya virus and Eastern equine encephalitis virus.
Furthermore, ARPA-H has chosen a team led by the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station that will focus on data and tool integration across the program.

“HHS Needs to Match Speed of Cyber Threats to Better Protect Health Care”
Brian Mazanec-an alumnus of the Biodefense PhD Program, Schar School adjunct professor, and Deputy Director of ASPR’s Office of Preparedness-recently discussed his office’s tools to help address cyber threats in healthcare at the GovCIO Media & Research’s 2024 Health IT summit. Read more and watch here.
“COVID-19: HHS Needs to Identify Duplicative Pandemic IT Systems and Implement Key Privacy Requirements”
This new study from the Government Accountability Office (GAO) reviews HHS’ efforts to “reduce unnecessary duplication, overlap, or fragmentation in the systems it uses to collect this kind of data, and its efforts to protect personal information.” It finds that HHS lacks a comprehensive list of these systems, and that it has not identified nor reduced unnecessary duplication. Furthermore, GAO finds that HHS has not fully implemented key privacy safeguards for the nine systems the Office reviewed.
“Strengthening Democracy and Pandemic Preparedness Go Hand in Hand”
This article in The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists was authored by John Bridgeland, Elizabeth (Beth) Cameron, J. Stephen Morrison, Jennifer B. Nuzzo, and Aquielle Person. In it, they argue “American democracy and public health effectiveness are inextricable. American health security depends on maximizing the ability to live in a free, pluralistic society able to coherently manage a public health emergency. In turn, the health of US democracy depends on citizens’ faith and trust in institutions—especially government—to protect them in a crisis such as a pandemic. Given disease threats like mpox or H5N1 avian flu, the looming potential for a worst-case biological crisis begs for a well-prepared nation. Unfortunately, the United States, because of or despite the challenges of the COVID pandemic, is now more politically polarized and less prepared to mount a united response to a major health emergency. That is a collective danger that threatens Americans and imperils the world.”
“The 2024 U.S. Elections: An Existential Crossroads for Global Health Policy”
Benjamin Mason Meier, Neha Saggi, Muhammad Jawad Noon, and Xinshu She breakdown the United States’ importance in global health and what all is on the line in this regard during the upcoming presidential election in this article for Global Health Now: “The 2024 U.S. elections will shape the future of global health policy, determining whether the nation will continue to provide crucial leadership to advance global health. Yet, with only passing mention of the field’s challenges in the presidential debate, the global health community must raise awareness of the global health positions of U.S. political candidates.”
“Republican Governors on International Pandemic Plan: We Will Not Comply”
Route Fifty’s Kaitlyn Levinson discusses a recent joint statement from 24 republican governors regarding the WHO’s pandemic agreement in this article: “In yet another example of how all things related to the pandemic have become political, nearly all of the country’s Republican governors have expressed their staunch opposition to a World Health Organization agreement about how nations should collectively prevent, prepare and respond to future global public health emergencies.”
“‘Not Enough Progress’ Made at 11th Round of Pandemic Agreement Talks”
Kerry Cullinan breaks down recent rounds of negotiations on the WHO’s pandemic agreement in this piece for Health Policy Watch. Cullinan explains in part, “According to the latest draft of the pandemic agreement, the most controversial part of the agreement – developing a pathogen access and benefit-sharing (PABS) system (Article 12) – will now be addressed via a separate “instrument”…The provisions governing the PABS system – described as a “multilateral system for safe, transparent, and accountable, access and benefit sharing for pathogens with pandemic potential” – will be developed by the Conference of the Parties (COP). This COP will be set up after the World Health Assembly has adopted the pandemic agreement.”
“How to Prevent the ‘Grand Pandemic'”
This Devex article summarizes a recent World Bank report-“Stopping the Grand Pandemic: A Framework for Action.” In the report, “…the World Bank argues that addressing AMR must become a critical priority for governments and their development- and private-sector partners. It also highlights strategies for helping address AMR through holistic and sector-led interventions and unlocking finance to fund them. A menu of specific technical, operational, and financial considerations helps guide government action to prevent AMR.”
“Modern Biosurveillance Methods: A Lay Introduction to Effective Use of Nucleic Acid Methods”
From the RAND Corporation: “The devastating impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led governments, health care institutions, and researchers to intensify their focus on developing improved means to detect, contain, and manage potential future outbreaks. As part of these efforts, policymakers and other nontechnical personnel need to understand available biosurveillance technologies. In this report, the authors summarize how current and emerging nucleic acid biosurveillance techniques work, describe their capabilities and limitations, and discuss the promise of emerging technologies.”
“Biosurveillance systems are used to detect, monitor, and characterize health threats, or pathogens, in human and animal populations, food, wastewater, and the environment. Nucleic acid testing assesses nucleic acids, comprising deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), to determine the biologic agents present in clinical samples (i.e., a sample collected by a medical laboratory from a symptomatic human) or environmental samples (e.g., wastewater).”
“The authors describe a scenario of testing for pathogens in wastewater that uses detection technology within a comprehensive and pathogen-agnostic biosurveillance system. Wastewater testing offers a method for collecting samples without needing symptomatic individuals to present at clinics for care. Such testing can, therefore, offer data prior to symptoms and from those who have less access to clinical care. The case study demonstrates the advancements needed to develop a truly pathogen-agnostic, cost-effective wastewater biosurveillance system.”
“The authors conclude that policymakers interested in establishing a biosurveillance program should carefully evaluate their specific research questions and their resource limitations to determine which technology is best suited to their needs.”
CEPI Biosecurity Strategy
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations recently released its new Biosecurity Strategy “…aimed at bolstering global health security and underscoring its commitment to tackling emerging epidemic and pandemic threats, whether they arise naturally, accidentally or through deliberate misuse.”
According to the coalition, “The strategy, published during United Nations General Assembly High-level Week 2024 in New York, will harness cutting-edge technologies and foster international collaboration to mitigate the risks posed by emerging pathogens. Its launch is a significant step in CEPI’s evolution, positioning it as a thought leader in the rapidly-developing fields of biosafety and biosecurity.”
“Team-Based Learning and Threshold Concepts in Biological Security and Dual-Use: Toward a Transformative Biological Security Pedagogy—The Game Changing Implications of CRISPR/Cas and the Design of a Novel Methodology for Influencing the Culture of Life and Associated Science through Awareness Raising and Education”
Simon Whitby, Malcolm Dando, Rebecca McCarter, and Simon Tweddell published this article in Creative Education: “CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) gene editing technologies appear to be a game-changer and suggest great potential for genome manipulation and for developments in next-generation therapeutics. Ethical, legal and social concerns have been raised in light of recent applications in humans. Concern also arises in relation to the potential of such developments for misuse. In addressing the post-COVID19 challenges raised by responsible research innovation and in confronting what to do about the vexed question of “dual-use”, we contend that awareness-raising and education concerning the ethical, legal and social implications of scientific research innovation represents a welcome and empowering alternative to top down regulatory responses that may serve to stifle innovation. The design and subsequent implementation of a novel transformative pedagogy combining Team-Based Learning and Threshold Concepts yields both empirical evidence-based metrics for real-time learning. As well as generating novel empirical data-sets for the identification of subject-specific threshold concepts across discrete specialisms in the life sciences, we argue that this hybrid methodology can be used to engage science professionals and students alike in meaningful and much-needed dialogue about developments relating to genome manipulation. We demonstrate how evidence-based threshold concepts can inform the design of bespoke subject-specific training as we suggest was the case from our deployment of team-based learning and threshold concepts during our proof of concept application, prior to the pandemic, during the course of two European Union Human Brain Project training programmes undertaken in 2017 and 2018, with experts in neuroscience research at the Karonlinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.”
“A New Risk Index to Monitor AI-Powered Biological Tools”
This post from RAND Europe discusses a collaboration with the Centre for Long-Term Resilience, explaining that the two organizations “…are collaborating to develop a new approach to assess the risks posed by AI-enabled biological tools. We will develop a risk index that assesses current risks from tool capability, tool evolution and maturity, to enablement of bioweaponisation that could result in biosecurity risks. Our index also takes into account how these risks may change over time in this rapidly evolving area. Our work will expand upon and update previous work conducted by CLTR on tool categorisation (Rose & Nelson 2023) and risk assessment (Moulange et al. 2024).”
“Food, Climate Change and National Security: The Feeding Resilience Plan and USAID’s Feed the Future Accelerator”
Tom Ellison and Noah Fritzhand recently published this Council on Strategic Risks blog post discussing the Council’s new Center for Climate and Security (CCS) report and the new US food security policy initiative. They explain in part “Attendees and panelists discussed the stability benefits of US agricultural innovation, the role of international legal frameworks on weaponization of food, the role of food security in US-China relations, and the criticality of US interagency collaboration on food security. Read the Feeding Resilience storymap and full report for analysis and recommendations endorsed by 30+ national security leaders, including former US combatant commanders, ambassadors, intelligence leaders, and heads of USAID and the World Food Program.”
“Strategic Stockpiling: How New State Policies will Impact Emergency Preparedness”
Maggie Nilz offers an overview of the Strategic National Stockpile in this blog post from the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials: “Preparedness is a vital component of public health, especially in the wake of the Mpox response and ongoing H5N1 outbreak. As states work to implement lessons learned from these events, stockpiling essential supplies is a critical part of the discussion. Stockpiling ensures that resources are available during emergencies allowing for a swift and effective response. To enhance preparedness policy, it’s important to understand the history of the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS) and how it has shaped recent state readiness legislation.”
“23andMe Is in Trouble. What Happens to All the DNA Data?”
The hosts of NPR’s All Things Considered talk 23andMe’s potentially looming collapse and what is likely to happen to the data of its more than 14 million customers if the company goes under in this clip.
ICYMI: Capitol Hill Steering Committee on Pandemic Preparedness and Health Security-The Current Mpox Crisis and Congress’s Role in Protecting the US from Health Security Threats
This event was hosted by the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security on September 18. At it, a panel of experts from government, industry, and academia discussed the US government’s response to the current mpox emergency. Learn more and watch the event recording here.
NEW: Bio and Beer (October 10)
From the Northern Virginia BioHub: Join us for a panel discussion with local investors as they share their funding priorities, insights on what’s ahead, and tips for meaningful engagement. Also, connect with our dynamic community of professionals from industry, academia, healthcare, investment, and government for a fun evening of networking!
Our panelists include:
- Deborah Hemingway, Managing Partner, Ecphora Capital
- Bibhash Mukhopadhyay, Managing Partner, Sound Bioventures
- Kevin O’Connell, Senior Vice President, In-Q-Tel
Register to attend for free at: https://ibi.gmu.edu/event/october-2024-bio-beer/
Location: JLL Tysons Office, 1800 Tysons Boulevard, McLean, Virginia 22102
Hosted by: The Northern Virginia BioHub
Signature Sponsor: JLL
Additional Sponsors: Virginia Bio, the Prince William County Department of Economic Development, and George Mason University’s Institute for Biohealth Innovation
Responsible AI: Design, Development, and Use
Join the Mason Autonomy and Robotics Center (MARC) for this 3-day in-person course on Responsible AI: Design, Development, and Use! As AI becomes increasingly pervasive across various domains, it is essential that we prioritize responsible principles, policies, and practices. Learn from top AI scholars and industry experts about ethical and safe AI deployment. You’ll also gain the critical skills to navigate the complexities of AI in business, healthcare, transportation and more.
Course Dates: October 15-17, 2024
Registration Deadline: October 8, 2024
FLUency: True Expertise and Effectiveness in the Battle Against Influenza
“This Commission meeting, FLUency: True Expertise and Effectiveness in the Battle Against Influenza, will be held on Tuesday, October 8th, in Washington, DC. The focus of this meeting will be to provide the Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense with a better understanding of: (1) national leadership to defend food and agriculture against influenza; (2) federal operational requirements for preparedness, coordination, and response; (3) biosurveillance, forecasting, and the need for diagnostic tests; and (4) front-line needs and partnerships in the fight against influenza.”
This event will take place in-person on October 8 from 9:20 am to 2 pm EST. Learn more and register here.
Register now: https://bit.ly/3zMvZOR
External Review of Ethical, Legal, Environmental, Safety, Security, and Societal Issues of Engineering Biology Research and Development
From NASEM: “Engineering biology holds significant potential to transform the U.S. and global economy, with promise to deliver innovative solutions in health, climate, energy, food and agriculture, and more. As research and development in engineering biology and other areas of the bioeconomy advance, addressing the societal issues related to these technologies is imperative. As requested by the CHIPS and Science Act, this study will conduct an evaluation of the ethical, legal, environmental, safety, security, and other societal issues related to engineering biology, and make recommendations on research needs related to these issues and means to effectively incorporate their consideration into research practice.”
“The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) will appoint an ad hoc committee to review and make recommendations on the ethical, legal, environmental, safety, security, and other appropriate societal issues related to engineering biology research and development. The committee will address the scholarship and practice of addressing these issues, focusing specifically on:
(1) An assessment of the current knowledge and practice on assessing and mitigating various societal issues including ethical, legal, environmental, safety, and security issues.
(2) A description of the gaps and needs relating to such issues, focusing on approaches for co-generation of assessment approaches and design of products, technologies, and services with users of engineering biology research and development
(3) Actionable recommendations on how the National Engineering Biology Research and Development Initiative, established by the CHIPS and Science Act, can address the identified gaps and needs.
(4) Actionable recommendations on how researchers across the range of disciplines engaged in engineering biology can best incorporate considerations of such societal issues into the development of research proposals and the conduct of research.”
“NASEM will produce a consensus report presenting the results of its work and offering its findings, conclusions, and recommendations.”
“We invite you to submit suggestions for experts to participate in this activity. The call for experts closes on October 16, 2024 at 11:59 (ET).”
Recommend an expert here.
DARPA Invites Proposals for AI Biotechnology Pitch Days Dec. 5-6
“DARPA funds the research and development of technologies with the potential for transformational impact, central to delivering on the agency’s mission to create and prevent strategic surprise for national security. The agency’s Biological Technologies Office focuses on the natural world to derive revolutionary capabilities centered on:
- Foundational technologies that promote simulation and prediction of biological systems and outcomes, like simulation, foundational models, and data generation,
- Warfighter readiness, health, and recovery, such as medical countermeasures, diagnostics, health IT and medical devices, and
- Operational support of U.S. forces to enable their execution of missions across the spectrum, ranging from fibers for garments to distributed, point-of-need manufacturing.”
“To capitalize on these new opportunities and further accelerate the pace of scientific and technological discovery and development, DARPA looks to include targeted and limited-scope investments via an AI BTO solicitation seeking proposals on technologies focused at the intersection of artificial intelligence and biotechnology.”
‘“AI BTO seeks to fund proposals that catalyze the formation of future research projects by clarifying the opportunity space and de-risking technical barriers to achieving high impact,” said BTO Director Dr. Michael Koeris. “To this end, the office is providing $4.5 million to support up to 45 revolutionary catalyst projects and will be finalizing research agreements day of. We look forward to reviewing the novel biotechnology approaches to further our national security mission.”’
“BTO leadership is interested in engaging first-time or non-traditional proposers and seeks revolutionary approaches to emerging or anticipated Department of Defense challenges. During these events, BTO will introduce five new overarching topics that align with AI/ML applications:
- Prediction and Health
- Autonomous Science
- Biomanufacturing/Synthetic Biology
- Challenges with Scale
- Exciting Frontiers”
Pitch Days
“DARPA will host AI BTO Pitch Days on December 5-6, 2024, in the Washington, DC, region to select and award AI BTO catalyst projects. To be considered for AI BTO Pitch Day participation, offerors must submit a short white paper consisting of a technical description of the proposer’s idea in response to one of the focus areas listed above.”
“DARPA will notify offerors if they are selected for further evaluation via an in-person Pitch Day presentation to a panel of BTO program managers at the AI BTO Pitch Day event.”
“If selected for award at Pitch Day, DARPA may issue a Research Other Transactions award for one of three award scenarios – $100,000, $200,000, or $300,000. The maximum amount of government funding given to any single proposer will be $300,000.”
“To submit a white paper, register at https://usg.valideval.com/teams/aibto_2024/signup. The deadline is Friday, October 9, 2024 by 4:00PM EDT. Late applications will not be accepted.”
“Additional information is available on SAM.gov.”
BWC Advanced Education Course
“State Parties, particularly from the Global South, often lack the resources, knowledge, and expertise to participate in the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) diplomatic process more meaningfully. To address this challenge, UNIDIR, Diplo Foundation and FRS are organizing the BWC Advanced Education Course (BWCedu).”
“The course will equip key stakeholders – government officials in capital with responsibilities in BWC implementation, aspiring and active diplomats and life scientists working on BWC issues and biological threats – with the essential knowledge, skills and expertise to actively participate in the BWC diplomatic process and thus contribute to a stronger and more effective Convention.”
“The BWCedu comprises a five-month advanced education programme. Through this programme, 25 participants will gain in-depth knowledge of the Convention, the diplomatic landscape and relevant scientific advancements.”
“The course will employ diverse learning methods, including online lectures, real-time engagement through webinars with experts and Working Group delegates and a week-long interactive in-person session in Geneva. Course participants will be provided with access to a collection of resources and information to support independent study on aspects of the BWC.”
“In its first iteration, the comprehensive programme will focus on the current Working Group agenda items, including the two mechanisms on science & technology and international cooperation and assistance being developed for consideration at the Tenth Review Conference, or earlier at a Special Conference if requested by a majority of State Parties. The course will prepare participants for ongoing engagement in the evolving framework of the BWC, empowering them to contribute to informed decision-making.”
Applications close on September 29. Learn more and apply here.
Call for Experts – Technical Advisory Group on Laboratory Services, Systems and Diagnostics in Health Emergencies
“The World Health Organization (WHO) is seeking experts to serve as members of the WHO Technical Advisory Group on Laboratory Services, Systems and Diagnostics in Health Emergencies (TAG-LAB). This “Call for experts” provides information about the advisory group in question, the expert profiles being sought, the process to express interest, and the process of selection.”
“Well-functioning and sustainable laboratory services, systems and diagnostics, operating according to international principles of equity, quality and safety, are essential to implement the International Health Regulations (2005)1 and achieve global health security. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently published the health emergency prevention, preparedness, response and resilience (HEPR) framework, describing the critical role of the laboratory to implement Collaborative Surveillance.”
“Laboratories also provide essential data to guide clinical care and inform coordination operations, as well as public health and social measures, in a range of emergency situations including outbreaks of pandemic and epidemic prone pathogens and humanitarian settings involving conflict, protracted crises and natural or man-made disasters. Considering this, a global strategy focused on laboratory services, systems and diagnostics for health emergencies is needed to address all of these contexts.”
“This strategy will connect global efforts and advance implementation of the laboratory components of the HEPR framework and World Health Assembly (WHA) Resolution 74.7 on strengthening WHO preparedness for and response to health emergencies that called for countries to “strengthen laboratory-based detection capacities”.”
“In this context, WHO is establishing a Technical advisory group on laboratory, services, systems and diagnostics for health emergencies (“TAG-LAB”). The TAG-LAB will act as an advisory body to WHO in this field.”
“The TAG-LAB is multidisciplinary, with members who have a range of technical knowledge, skills and experience relevant to virus evolution. Up to 25 Members may be selected. WHO welcomes expressions of interest from experts in laboratory services, systems or diagnostics, clinical scientists, academic researchers, healthcare professionals, or others with expertise in one or more of the following areas:
- Laboratory Systems
- Laboratory Services
- Diagnostics
- National and International Policy, Regulation and Guidance
- Biosafety
- Biosecurity
- Bioinformatics
- Clinical Management
- Outbreak Preparedness, Response and Resilience
- Emergency response in humanitarian settings involving conflict, protracted crises and natural or man-made disasters
- Academic Research
- Public Health
- Virology, Microbiology, Mycology, and Emerging or Re-emerging diseases”
Learn more and submit and expression of interest here by September 30.
Call for Experts: Health-Security Interface Technical Advisory Group (HSI-TAG)
“The World Health Organization (WHO) is seeking two experts to serve as new members of the Health-Security Interface Technical Advisory Group (HSI-TAG). This “Call for experts” provides information about the advisory group in question, the expert profiles being sought, the process to express interest, and the process of selection.”
“The concept of Health-Security Interface (HSI) applies to those public health activities whose performance involves to some extent the security sector broadly understood (e.g. international and non-governmental organizations, civil defense, military health personnel, law enforcement and armed forces, defense-related research programmes), certain international organizations and other entities with a security relevant mandate. These activities may include protection of health from traditional and emerging infectious disease threats; deliberate events and investigation of alleged use of chemical and biological agents including non-permissive environments and conflict zones; and any health activities performed in collaboration with security actors.”
“The HSI-TAG is multidisciplinary, with members who have a range of technical knowledge, skills and experience relevant to the Health-Security Interface.”
“Considering the recent developments and global trends, the Secretariat realized that there was a need to strengthen the following areas of expertise/experience, hence welcomes expressions of interest from:
- Bioterrorism experts (knowledge on pathogens of security concern, their microbiological characterization and application/modification for weaponization, diagnostics, countermeasures and containment measures),
- Decision/policy makers with hands-on experience dealing with significant deliberate event(s) (biological/chemical) response at the local, regional, or national level.”
“For the improved geographical and gender representation of the HSI-TAG members, the WHO Secretariat encourages applications from the WHO African, Western Pacific, European, Eastern Mediterranean and Pan American Health Organization/Americas regions and female or non-male gender identities.”
Learn more about the HSI and express interest by October 7 here.
