This edition of the Pandora Report focuses on public and global health developments from the first week of the second Trump administration. This includes the executive order to withdraw the US from the WHO, the pause on communications from the Department of Health and Human Services, and more.
HHS Formally Debars Peter Daszak and EcoHealth Alliance
Last week, following eight months of investigation, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) severed all funding and formally debarred EcoHealth Alliance Inc. and its former president, Dr. Peter Daszak, for a period of five years. House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform Chairman James Comer said in a statement about the formal announcement that, “Justice for the American people was served today. Bad actor EcoHealth Alliance and its corrupt former President, Dr. Peter Daszak, were formally debarred by HHS for using taxpayer funds to facilitate dangerous gain-of-function research in China. Today’s decision is not only a victory for the U.S. taxpayer, but also for American national security and the safety of citizens worldwide.”
He continued, “In May 2024, Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic Chairman Brad Wenstrup released evidence that EcoHealth repeatedly violated the terms of its NIH grant. EcoHealth routinely ignored government oversight requests, failed to report dangerous gain-of-function experiments conducted at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, and produced a required research report two years late. HHS cited all of these discoveries as key reasons for formally debarring EcoHealth and Dr. Daszak. Given that a lab-related incident involving gain-of-function research is the most likely origin of COVID-19, EcoHealth and its former President should never again receive a single cent from the U.S. taxpayer.”
RFK Jr. Petitioned FDA to Revoke COVID-19 Vaccine EUAs
The New York Times reported last week that Robert F. Kennedy Jr., President Trump’s pick to lead HHS, filed a petition with the FDA in May 2021 that demanded the agency rescind emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 vaccines and refrain from approving any such vaccines in the future. In the petition, Kennedy and Meryl Nass (a physician on the Children’s Health Defense Scientific Advisory Board, an organization founded by Kennedy), claimed, in reference to COVID-19 vaccines in 2021, that “…the current risks of serious adverse events or deaths outweigh the benefits, and because existing, approved drugs provide highly effective prophylaxis and treatment against COVID, mooting the EUAs.”
These “effective prophylaxis and treatment” drugs include ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine, both of which had already been proven ineffective against COVID-19. Furthermore, at the time the petition was filed, some estimates were already showing that the rapid rollout of these vaccines had saved around 140,000 lives in the US alone. While the petition garnered little attention at the time, it is now a demonstration of the profound lack of understanding RFK Jr. has of medicine and public health. His confirmation hearing as the nominee to become the Secretary of HHS is scheduled for January 29.
Trump Issues Executive Order to Withdraw the US from the WHO
On January 20, President Trump issued an executive order stating the intention of the US to withdraw from the World Health Organization. The order explains in part, “The United States noticed its withdrawal from the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2020 due to the organization’s mishandling of the COVID-19 pandemic that arose out of Wuhan, China, and other global health crises, its failure to adopt urgently needed reforms, and its inability to demonstrate independence from the inappropriate political influence of WHO member states. In addition, the WHO continues to demand unfairly onerous payments from the United States, far out of proportion with other countries’ assessed payments. China, with a population of 1.4 billion, has 300 percent of the population of the United States, yet contributes nearly 90 percent less to the WHO.”
However, these numbers are at odds with those tallied by the WHO itself. While President Trump asserted that the US gives the WHO $500 million in contrast to $39 million from China, the US was set to contribute $706 million while China is at $184 million in the organization’s 2024-25 budget.
Furthermore, WHO funding comes from two pots. The first is based on the UN’s assessment of a country’s “capacity to pay,” which is calculated based on countries’ populations and wealth. For the US and China, these numbers are sat at $264 million and $181 million respectively. This pot makes up less than 20% of WHO’s budget. The other, much larger pot, involved voluntary contributions that come not just from member states, but from philanthropic organizations, corporations, NGOs, and even private citizens. The US is projected to contribute $442 million to this fund, while China is on track to contribute just $2.5 million. While China is not contributing as much as the US, it is meeting its assessed contributions capacity to pay as determined by the UN. (Source: NPR)
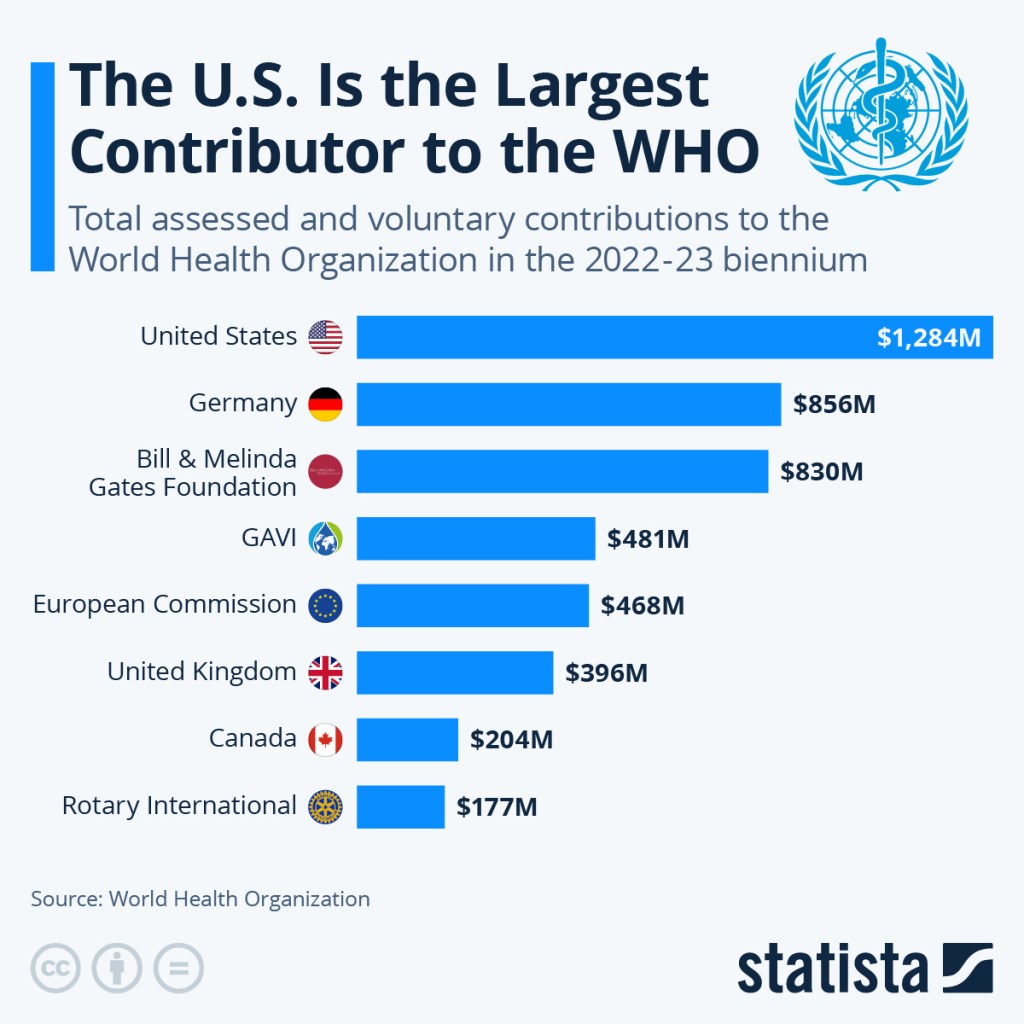
As the EO alludes to, Trump tried to withdraw the US from the WHO during his first administration, with his administration formally notifying the UN Secretary-General of this intention on July 6, 2020. The United States entered into WHO membership in 1948 following a joint resolution of Congress. This resolution was signed by President Truman, who then used this to sign the Instrument of Acceptance of the Constitution of the World Health Organization. Because of this, there are questions about the legality of this 2020 order.
Some have cited the ruling in Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer as a legal precedent that would prevent Trump’s unilateral withdrawal from WHO. In this case, the US Supreme Court found that President Truman lacked statutory authority conferred by Congress (or the Constitution) in seizing control of steel production during the Korean War. Justice Hugo Black wrote in the majority opinion, “When the President takes measures incompatible with the expressed or implied will of Congress, his power is at its lowest ebb…”
This has formed the basis for legal arguments against Donald Trump’s previous efforts to withdraw the US from WHO membership as withdrawing without express approval from Congress would therefore violate US law. This is in addition to requirements for the US to pay its financial obligations to the WHO for the current fiscal year.
Perhaps most importantly, US withdrawal from the WHO would harm global health as a whole and represent yet further decline of US global leadership. Severing this relationship would only be detrimental to global health, which certainly cannot be good for the United States as it will undermine the country’s capacity to respond to health emergencies. Furthermore, this move would weaken US influence and diplomacy. This would also potentially present China with a greater opportunity to take leadership and reshape global norms to suit its interests, something that President Trump should be worried about.
The World Health Organization is not perfect, and it never will be. The way to address problems in the WHO, however, is by working collaboratively with the organization itself and other Member States. This has proven effective over the last several years, during which WHO has implemented the largest set of reforms in its history. The US will lose its leverage in pushing for reform by abandoning its membership, and it will also lose its place in an organization that has helped make the world a safer, healthier place for everyone.
Further Reading: “Memo to Trump: Invest in Global Health Security,” Saskia Popescu, The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists
Trump Administration Halts Federal Health Agencies’ Communications
The Trump administration has ordered federal health agencies to pause all external communications through February 1, including health advisories, weekly scientific reports, updates to websites, and social media posts. The instructions provided to staff at HHS agencies (including the FDA, CDC, and NIH) cited a review as the reason for this pause, though it is broader in scope than expected.
As The Washington Post explains, “The pause on communications includes scientific reports issued by the CDC, known as the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR); advisories sent out to clinicians on CDC’s health alert network about public health incidents; data updates to the CDC website; and public health data releases from the National Center for Health Statistics, which tracks myriad health trends, including drug overdose deaths.”
One anonymous official told the Post that CDC was scheduled to publish several MMWR reports this week, three of which are about H5N1 avian influenza. It remains unclear if this guidance exempts urgent communications for things like foodborne disease outbreaks, drug approvals, or new bird flu cases, though the memo explains some exceptions can be made on a case-by-case basis.
Trump Freezes NIH Meetings, Travel, and Hiring
President Trump’s administration has also implemented far-reaching pauses at the NIH. In addition to the overarching pause on HHS communications, the administration has cancelled NIH meetings like grant review panels in addition to placing a freeze on hiring (which is in effect across the federal government) and an indefinite ban on travel. Science Insider describes the confusion and uncertainty this has caused, writing in part “…officials halted midstream a training workshop for junior scientists, called off a workshop on adolescent learning minutes before it was to begin, and canceled meetings of two advisory councils. Panels that were scheduled to review grant proposals also received eleventh-hour word that they wouldn’t be meeting.”
These pauses have reportedly left many at NIH and elsewhere with great uncertainty and unease. Many research meetings with teams of people at numerous institutions were cancelled suddenly, delaying important work. The travel pause can be especially damaging for younger scientists, including graduate students and postdocs, who need conference presentations to get feedback on their work and network in their fields. The travel pause also prevents NIH employees from traveling to other NIH locations, and has required some already traveling to return home prematurely.
Possible Executive Order Pausing Gain of Function Research Funding Ahead
The Trump administration is reportedly drafting an executive order that would pause federal funding for gain of function research. In 2014, the NIH imposed a moratorium on federal funding for certain studies involving GoF research. This stemmed from concerns about two studies involving modified H5N1 viruses and concerns about safety issues at CDC and NIH. Furthermore, the NIH stated at the time that this moratorium would “…be effective until a robust and broad deliberative process is completed that results in the adoption of a new US Government gain-of-function research policy.” By 2017, the National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB) had developed a framework for assessing funding decisions for research that involved enhanced potential pandemic pathogens.
Debate over federal funding for this kind of research grew once again amid the COVID-19 pandemic. This has included multiple congressional hearings, commentary, and the introduction of a bill in the Senate, the Viral Gain-of-Function Research Moratorium Act. The Biden administration released in May 2024 the United States Government Policy for Oversight of Dual Use Research of Concern and Pathogens with Enhanced Pandemic Potential, which the NIH recently released guidance on. However, the executive order is expected to supersede at least a portion of this policy.

New Book on Gain of Function
Nicholas Evans, Associate Professor and Chair of the Department of Philosophy at the University of Massachusetts Lowell, has a new book out that examines the controversial and poorly understood domain of “gain of function” research. Published by MIT Press, Gain of Function describes what this kind of research is, what it isn’t, and why a small number of scientific experiments continue to make headlines. The book explains what gain-of-function research means in science and in the context of government policy, traces the history of the original research that sparked the initial controversy, and describes efforts to assess the risks and benefits of this research and to regulate it. The book concludes with Evans’ assessment of the future of gain of function, including how debates about this type of research will influence politics, science and public health for years to come. Use the promo code MITPCONF for a 30% discount.
New NSABB Working Group on in silico Research and Computational Models
The National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB) has established a new Working Group on in silico Research and Computational Models. The working group, co chaired by Rachel Levinson of Arizona State University (and chair of the NSABB) and Sarah Carter of Science Policy Consulting LLC, is “charged with developing strategies for identifying, and options for mitigating, potential risks associated with in silico research, computational models (including biological design tools), and datasets in life sciences settings. The NSABB is to especially focus on identifying approaches that could inadvertently or deliberately result in the development of dual-use information or models directly enabling the design of a pathogen with enhanced pandemic potential (PEPP) or a novel biological agent or toxin that could pose significant threat to public health, including datasets that could be used to develop such models and in silico experiments that could meet the definition of dual use research of concern (DURC) outlined in the Policy. In conducting this evaluation, the NSABB should consider how in silico research and computational models could enable the design, development, enhancement, or acquisition of transmissible biological agents with specific attributes, such as increased virulence, transmissibility, environmental survivability, immune evasion, difficulty of detection and attribution, or similar characteristics.”
“Envisioning an Independent Bioresponsibility Authority to Safeguard U.S. Leadership in the Life Sciences”
From the Scowcroft Institute: “This report by the Texas A&M Biosecurity and Pandemic Policy Center proposes an independent federal agency to oversee the safety and security of pathogen research conducted in the United States or funded by the U.S. government. Taking a more comprehensive and collaborative approach, the agency would pair expanded regulatory oversight with technical assistance, non-punitive incident reporting, funding for biosafety and biosecurity research, and education and training efforts. It would consolidate and streamline requirements and remain flexible as technology advances. This approach to the safe, secure, and ethical conduct of life science research merits a new term: bioresponsibility.”
“Global Risks Report 2025”
This edition of the World Economic Forum’s Global Risk Report “…reveals an increasingly fractured global landscape, where escalating geopolitical, environmental, societal and technological challenges threaten stability and progress.” It includes a section on biotech and the challenges posed by the current lack of global ethical boundaries for biotech developments.
“Russia Used Chemical Weapons 434 Times in December, Ukraine’s General Staff Says”
This article from the Kyiv Independent analyzes recent reporting from the General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces. It explains in part, “Russia has been intensifying its use of chemical agents on the battlefield in Ukraine. A Kyiv Independent investigation from August 2024 showed that instances of gas attacks are rising, and the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) confirmed on Nov. 18 that a riot control agent known as CS has been used in Ukraine.”
“Fact-Checking Russia’s Claims on Chemical Weapons”
In this piece from Vox Ukraine, John V. Parachini, Khrystyna Holynska, and Kateryna Ionova breakdown Russia’s CW disinformation and attempts to abuse its leadership position within OPCW: “For years, Russia positioned itself as a staunch advocate for the nonproliferation of chemical weapons. By asserting that it had eliminated the largest stockpile of chemical weapons and actively worked to deter other countries from developing and using them, Russia claimed to have a right to a leadership position in the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW). When accusations arose against Russia or its allies regarding the contrary, Russia vehemently denied all such claims and accused Western nations of orchestrating disinformation campaigns aimed at discrediting it.”
NEW: Advanced Data Sharing to Strengthen One Health Effectiveness: Building Trust for Effective Collaboration
From NASEM: “Applying a One Health approach requires collaboration at multiple levels to address complex challenges. Actors, such as government agencies, non-government and private entities, citizens, and the research community must have reason to believe that they will receive benefits and credit for data shared without threat of retaliation, exploitation, or misapplication. Trust enables the free flow of information and resources between stakeholders and fosters an environment where diverse groups can unite towards a common goal. Without trust, efforts to tackle these challenges become fragmented and inefficient. In this webinar, invited speakers will share how their successful One Health programs establish and maintain trust, thereby supporting innovative solutions that no single discipline could achieve alone.”
This event will take place on January 28 at 4 pm EST. Learn more and register here.
NEW: The Future of Syria’s Chemical Weapons Stockpile
From the Arms Control Association: “The CWC Coalition will host a webinar on Wednesday, January 29 on the future of Syria’s chemical weapons stockpile after the fall of the Assad regime.”
“The collapse of the Assad regime and the resulting political transition in Syria leaves questions about the fate of the country’s remaining chemical weapons stockpile. Since 2022, high level disarmament discussions at the UN have repeatedly remarked on the “gaps, inconsistencies, and discrepancies” remaining in Syria’s declaration of its chemical stockpile, while human rights groups have pressed for justice for victims of the chemical attacks.”
“We will discuss how can the OPCW, CWC member states, and civil society can approach the transitional government as an opportunity to bring Syria into compliance with its obligations under the CWC, have accountability for perpetrators, and justice for victims.”
Gregory Koblentz, Director of the Biodefense Graduate Program, will be one of the speakers. His commentary will be based on his recent article with Natasha Hall, the other speaker, in Foreign Affairs.
This webinar will take place 10-11 am EST. RSVP here.
NEW: Schar School Open House
The Schar School of Policy and Government will be hosting an in-person Arlington Graduate Open House along with the Costello College of Business, Antonin Scalia Law School, and the Carter School for Peace and Conflict Resolution. Explore the different degree programs we offer at the master’s, doctoral, and professional levels, as well as our graduate-level certificates. Representatives will be in attendance to discuss our various graduate programs and how you can further your studies while continuing to work. Gregory Koblentz, Director of the Biodefense Graduate Program, will also be in attendance.
This event will take place on February 4 between 5:30 and 7 pm EST. Register here.
NEW: Biodefense MS Information Session
“Prospective students are invited to attend a information session to hear more about the Biodefense M.S. program offered at the Schar School. The online session will provide an overview of the program, as well as the application process, student experience and graduate outcomes. This session admissions will be led by the Graduate Admissions team.”
This sessions will take place at 12 pm EST on February 13. Learn more and register here.
Upcoming PACCARB Public Meeting
“The Presidential Advisory Council on Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (PACCARB) provides advice, information, and recommendations to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS Secretary). The council supports and evaluates U.S. government activities focused on fighting antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in human health, animal health, and environmental health. Using this One Health approach, members of the PACCARB have a wide range of backgrounds, including academia, industry, public health, advocacy, veterinary, and agricultural production.”
“The PACCARB was established under Executive Order 13676 and is included in the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness and Advancing Innovation Act of 2019 (PAHPAIA). Since 2019, the President of the United States has given authority to the HHS Secretary as the primary recipient of PACCARB recommendations. Additional information on the authority and activities of the PACCARB can be found on the About Us page in the charter.”
“As a federal advisory committee, the PACCARB looks to engage with the public and all AMR stakeholders. The council holds several public meetings every year both in person and live streamed on the HHS.gov website. These meetings are open to anyone with an interest in combating AMR.”
The next PACCARB Public Meeting will take place January 28-29 at the Ritz-Carlton, Pentagon City. Learn more and register to attend here.
Preparedness in Rural Communities: National and State/Local Perspectives and Plans
From Penn State: “The COVID-19 pandemic and recent hurricanes have thrust the preparedness of rural communities into the national spotlight. At the federal level, the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have recently released national goals and plans for preparedness of rural communities. The overall objective of this virtual, 2-day mini-symposium is to identify opportunities in public health and agricultural preparedness and response in rural communities. The mini-symposium will focus upon national perspectives on Thursday, January 30 and the state/local perspectives on Friday, January 31. Speakers include representatives of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response, the Department of Homeland Security, US Department of Agriculture, the USA Center for Rural Public Health Preparedness, and state/local leaders.”
This event will take place on January 30 and 31, from 11 am to 2 pm ET each day. Learn more and register here.
Rise of the Zombie Bugs: The Surprising Science of Parasitic Mind-Control
Johns Hopkins APL’s colloquium will feature Mindy Weisberger, author of the upcoming book Rise of the Zombie Bugs: The Surprising Science of Parasitic Mind-Control: “Zombies are all around us—insect zombies, that is. In Rise of the Zombie Bugs, Mindy Weisberger explores the eerie yet fascinating phenomenon of real-life zombification in the insect class and among other invertebrates. Zombifying parasites reproduce by rewriting their victims’ neurochemistry, transforming them into the “walking dead”: armies of cicadas, spiders, and other hosts that helplessly follow a zombifier’s commands, living only to serve the parasite’s needs until death’s sweet release (and often beyond).”
Learn more about this January 31 event here.
Cyberbiosecurity Summit
From Johns Hopkins APL and Bio-ISAC: “Advancements in biomanufacturing and biotechnology drive the science we need to thrive, everything from apples to vaccines. The Cyberbiosecurity Summit 2025 convenes leading experts in biotechnology, biosecurity, and cybersecurity to explore the intersection of these fields and discuss the strategies to create a safe, secure future for us all.”
This event will take place February 25-26 in Laurel, MD. Register here and review the call for sessions here (closes 12/12).
Sustainable Manufacturing: Building and Preserving a Resilient Medical Industrial Base
“Join industry and government partners for our second annual industry summit! During this event, leaders from IBMSC will share our strategic vision and organizational priorities. Speakers will also share potential opportunities for building and preserving the medical industrial base. This event will be in-person only and space is limited!”
This event will take place March 11-12 in Washington, DC. Learn more and register here.
Exciting Update: The BWC NIM Database Is Complete!
UNIDIR is glad to announce that the BWC National Implementation Measures Database, developed in partnership with VERTIC, has reached a significant milestone: profiles for all 187 States Parties to the Biological Weapons Convention are now live! This comprehensive online tool provides detailed insights into each country’s national implementation measures under the BWC, supporting transparency, trust, and international cooperation.
All profiles are available in English, and the team is committed to translating them into all official UN languages throughout 2025. Updates to the profiles will also be made regularly to ensure they remain accurate and relevant.
Explore the database at bwcimplementation.org.
Enhancing UK Biosecurity: DASA Launches Microbial Forensics Competition
“On behalf of the Defence Science and Technology Laboratory(Dstl), the Defence and Security Accelerator (DASA) is pleased to launch a new Themed Competition called Future-proofing Biosecurity by Strengthening the UK’s Microbial Forensic Capability. The competition is being run in response to the 2023 UK Biological Security Strategy which aims to implement a UK-wide approach to biosecurity that will strengthen deterrence and resilience to a spectrum of biological threats.”
“Dstl is leading the creation of the United Kingdom Microbial Forensics Consortium (UKMFC) which is being developed in support of the Detect Pillar of the Biological Security Strategy. It will comprise a network of biosurveillance laboratories from all four nations of the UK, operating under a One Health doctrine. This competition seeks novel technology options or technical approaches that can directly support the UKMFC initiative.”
Learn more and submit proposals here.
