This week’s edition of the Pandora Report covers news from the Biodefense Graduate Program, HHS’ announcement to cut federal funding to the EcoHealth Alliance, and more.
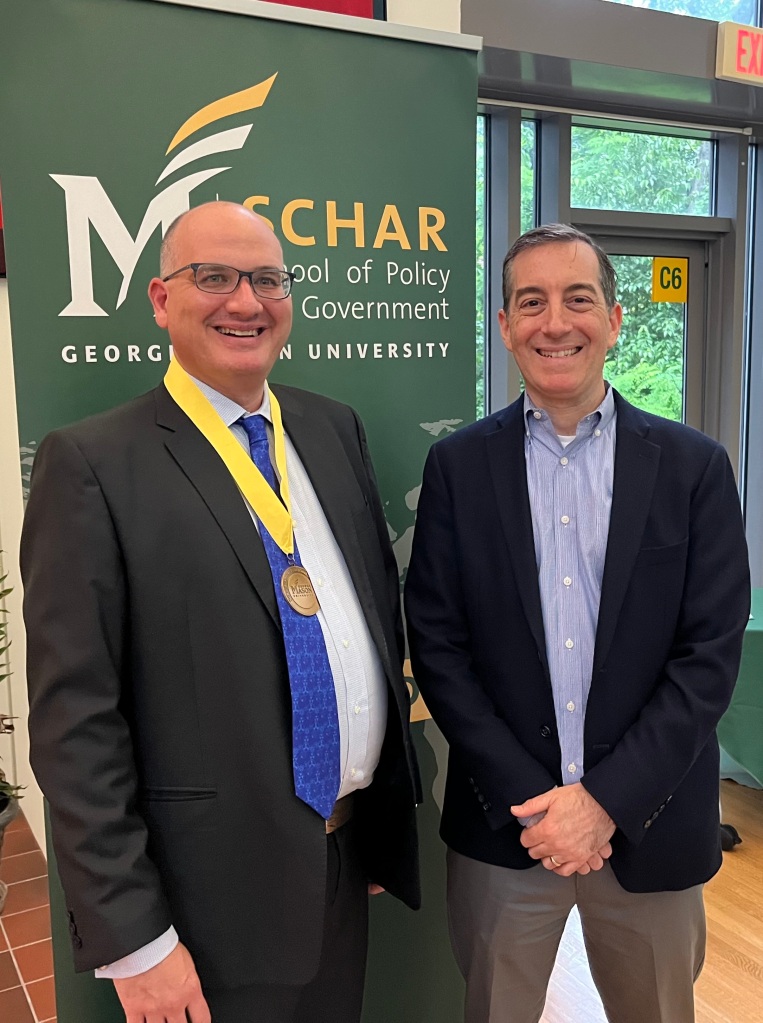
Biodefense Program Receives Gift from the CBRNE Industry Group
For the second year, the Schar School of Policy and Government at George Mason University received a generous gift from the CBRNE Industry Group, an association of organizations supporting chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and explosive defenses, to support the Biodefense Graduate Program. Program director Dr. Gregory Koblentz accepted the award on behalf of the Schar School and Biodefense Program at the CBRNE Industry Group’s annual dinner on May 15. The dinner’s keynote speaker was Rebecca Hersman, director of the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA).
Congratulations to Graduating Biodefense Students
Congratulations to the newly minted MS in Biodefense students who graduated from the Schar School this week: Abigail Danfora, Theresa Hoang, Emily Johnson, John Kisko, Nick Marko, Geoff Mattoon, Jack Moore, Miranda Nastasi, Brittany Novak, Olivia Parker, Max Towers and Jacob Wellerman. A special congratulations to Nick Marko for receiving the Outstanding Biodefense MS Student Award for his exemplary scholarship and to Olivia Parker for receiving the Frances Harbour Award in recognition of her community leadership in the Biodefense Program.



Biden Administration Moves to Ban Funding for EcoHealth Alliance
Following a tense Congressional hearing and the release of a highly critical select subcommittee interim report earlier this month, the Department of Health and Human Services announced in a letter on Wednesday that it is moving forward with debarment proceedings and implementing a government-wide suspension of federal funding for EcoHealth Alliance. This includes active grants, three of which totaled $2.6 million in NIH funding for EcoHealth Alliance last year. The NIH cited multiple failures on the part of the organization that it first reported three years ago, including EcoHealth’s failure to “promptly report findings from studies on how well bat coronaviruses grow in mice…”
House Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic Chairman Brad Wenstrup (R-OH) said in a statement about the announcement, ‘“EcoHealth Alliance and Dr. Peter Daszak should never again receive a single penny from the U.S. taxpayer. Only two weeks after the Select Subcommittee released an extensive report detailing EcoHealth’s wrongdoing and recommending the formal debarment of EcoHealth and its president, HHS has begun efforts to cut off all U.S. funding to this corrupt organization. EcoHealth facilitated gain-of-function research in Wuhan, China without proper oversight, willingly violated multiple requirements of its multimillion-dollar National Institutes of Health grant, and apparently made false statements to the NIH. These actions are wholly abhorrent, indefensible, and must be addressed with swift action. EcoHealth’s immediate funding suspension and future debarment is not only a victory for the U.S. taxpayer, but also for American national security and the safety of citizens worldwide.”
‘“The Select Subcommittee’s investigation into EcoHealth and the origins of COVID-19 is far from over. Dr. Daszak and his team are still required to produce all outstanding documents and answer the Select Subcommittee’s questions, specifically related to Dr. Daszak’s potential dishonesty under oath. We will hold EcoHealth accountable for any waste, fraud, and abuse and are committed to uncovering any illegal activity, including lying to Congress, NIH, or the Inspector General,” he continued.
EcoHealth Alliance said in a statement that it “is disappointed by HHS’[s] decision today and we will be contesting the proposed debarment. We disagree strongly with the decision and will present evidence to refute each of these allegations and to show that NIH’s continued support of EcoHealth Alliance is in the public interest.”

“China and Medical AI: Implications of Big Biodata for the Bioeconomy”
Caroline Schuerger, Vikram Venkatram, and Katherine Quinn recently published this CSET Issue Brief: “China supports medical artificial intelligence development to achieve bioeconomy leadership. Countries that strategically prioritize medical AI could benefit from an economic advantage and set global norms for future developments. Our new report examines China’s stated goals for medical AI, which range from the collection and protection of vast amounts of biodata, to facilitating research and development, to supporting medical AI commercialization. China’s comprehensive actions to prioritize medical AI development have major implications for U.S. economic and technological competitiveness.”
“China’s Industrial Clusters: Building AI-Driven Bio-Discovery Capacity”
Anna Puglisi and Daniel Chou recently authored this CSET Data Brief: “China is banking on applying AI to biotechnology research in order to transform itself into a “biotech superpower.” In pursuit of that goal, it has emphasized bringing together different aspects of the development cycle to foster multidisciplinary research. This data brief examines the emerging trend of co-location of AI and biotechnology researchers and explores the potential impact it will have on this growing field.”
“China’s Hybrid Economy: What to Do About BGI?”
Anna Puglisi tackles China’s industrial policy and BGI (formerly Beijing Genomics Institute) in this CSET blog post: “As the U.S. government considers banning genomics companies from China in the Biosecure Act, it opens a broader question of how the U.S. and other market economies should deal with China’s national champions. This blog post provides an overview of BGI and how China’s industrial policy impacts technology development.”
“Science and Technology Advisory Mechanism for the Biological Weapons Convention, A Proof-of-Concept Exercise”
From The Interacademy Partnership: “This document encapsulates the insights emanating from the recent ‘Proof of Concept Meeting for a Scientific Advisory Body for the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention’ (BWC) that IAP hosted in Trieste, Italy, on 27-28 February 2024.”
“The meeting, convened under the auspices of IAP and in coordination with the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), brought together 38 technical experts from 32 countries. Their deliberations focused on the potential impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on global biosecurity and international cooperation within the framework of the BWC. Participants stressed the need for a continuous review process to monitor AI trends, especially its implications for biology relevant to the BWC. The report serves as the report of a putative Science Advisor to the BWC, summing up the expert deliberations from the proof of concept meeting.”
“The release of “Science and Technology Advisory Mechanism for the Biological Weapons Convention, A Proof-of-Concept Exercise”, deriving from the proof of concept meeting, marks a key moment in the journey towards establishing a scientific advisory body for the BWC.”
“Read and download the Biosecurity Report here.”
“USDA, FDA Turf Battles Hamper Responses to Outbreaks Like H5N1 Bird Flu”
Rachel Cohrs Zhang, Lizzy Lawrence, and Nicholas Florko discuss federal agencies’ turf battles in this STAT News piece that includes information derived from interviews with more than 20 former federal officials. They explain in part, “Because H5N1 is currently an animal disease, it’s clearly the USDA’s responsibility to test cattle and get a handle on the outbreak. But already, public health experts are concerned that the scope of that agency’s testing regime is too limited. The department is requiring farmers test only lactating cows before moving them across state lines.”
‘“There needs to be a better understanding of the scope and scale of the problem,” said Stephen Ostroff, a former deputy commissioner in charge of food safety at the FDA. “This seems like it’s not necessarily going to be able to identify problems that could occur within a state.”’
Read more here.
“As Bird Flu Looms, the Lessons of Past Pandemics Take On New Urgency”
John M. Barry discusses lessons learned from the 1918 flu pandemic and other pandemics and their significance as bird flu continues to spread in this New York Times opinion piece. He writes in part, “While much would still have to happen for this virus to ignite another human pandemic, these events provide another reason — as if one were needed — for governments and public health authorities to prepare for the next pandemic. As they do, they must be cautious about the lessons they might think Covid-19 left behind. We need to be prepared to fight the next war, not the last one…Two assumptions based on our Covid experience would be especially dangerous and could cause tremendous damage, even if policymakers realized their mistake and adjusted quickly.”
“Rise of Drug-Resistant Superbugs Could Make COVID Pandemic Look ‘Minor’, Expert Warns”
This piece from The Guardian discusses warnings from Prof Dame Sally Davies, England’s former chief medical officer and the UK’s current special envoy on AMR. It explains, “She paints a bleak picture of what could happen if the world fails to tackle the problem within the next decade, warning that the issue is “more acute” than climate change. Drug-resistant infections already kill at least 1.2 million people a year…“It looks like a lot of people with untreatable infections, and we would have to move to isolating people who were untreatable in order not to infect their families and communities. So it’s a really disastrous picture. It would make some of Covid look minor,” said Davies, who is also the first female master of Trinity College, Cambridge.”
“Dissecting Pandemic-Prone Viral Families, Volume 4: The Pneumoviridae”
This document by Amesh A. Adalja for Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security covers the pandemic threats posed by the Pneumoviridae family: “The Pneumoviridae viral family, formerly a subfamily of Paramyxoviridae, consists of 2 genera: Orthopneumovirus, the members of which infect mammals, and Metapneumovirus, which are specific for either mammals or birds.”
“Pneumoviridae poses a largely underappreciated pandemic threat. Only 2 known viral family members infect humans: human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV, commonly RSV) and human metapneumovirus (HMPV).1 These 2 endemic respiratory viruses confer substantial morbidity and mortality on the human species, particularly among older adults and young children and across different sociodemographic strata.2 If a zoonotic or yet undiscovered viral family member acquired the ability to efficiently infect humans, it could spread prolifically, especially when faced with little immunity”
Read more here.
“Remarks by Dr. Liz Sherwood-Randall Assistant to the President for Homeland Security on Countering Bioterrorism in an Era of Technology Convergence”
Read Liz Sherwood-Randall’s remarks at the Ash Carter Exchange that focus on preventing bioterrorism and threats posed by rapidly advancing biotechnologies. She said in part, “And this frame of “preventive defense” – which identifies what we can do now to prevent far more pernicious threats from emerging in the future – is a guiding principle for me as we face the emergence of a whole new category of “A list” threats at the intersection of biology, engineering, and artificial intelligence.”
“Given my current duties as the President’s Homeland Security Advisor, this is a major concern because of the very real prospect that these technologies – which are largely out “in the wild” rather than controlled by governments – could be accessed and weaponized by terrorists with potentially catastrophic effects.”
“So, I chose to talk with you here today about what we can do to counter biological terrorism and other malicious uses of advances in biotechnology in this era of rapid technology convergence.”
“Getting Down to Science”
This USDA post by Stephanie Jacques discusses the work starting to take shape at the new National Bio and Agro-Defense Facility (NBAF). She writes in part “Science at NBAF is starting in phases. This phased process began with low-risk, common science practices that don’t involve infectious pathogens and is moving to more advanced or mission-focused science in later phases. As NBAF is ramping up science operations in Manhattan, Kansas, its predecessor — the Plum Island Animal Disease Center in New York — will continue protecting American agriculture until NBAF is ready to assume the center’s full mission.”
“Trumping Pandemic Preparedness”
Chelsea Cirruzzo and Ben Leonard recently published this piece in Politico that discusses former President Trump’s promise that, if re-elected, he will abolish the White House’s Office of Pandemic Preparedness and Response Policy. While they explain that he can not entirely get rid of the office on his own, they cover three ways he could undermine the office, including not appointing anyone to run or staff the office, asking Congress to overturn the law it passed creating the office, or reshaping the office to better suit his political interests.
“A ‘Plague’ Comes Before the Fall: Lessons from Roman History”
Colin Elliott discusses the effects of the Antonine plague in this piece, writing in part “The Pax Romana—the 200-year “golden age” of the Roman Empire—was a marvel of diversity, connectivity, and unchallenged hegemony. By the middle of the second century AD, imperial Rome ruled territory across three different continents. Roughly one-quarter of the Earth’s population, some 60 million people, lived under Rome’s vast aegis, and the emperors of the age—most notably Marcus Aurelius—enjoyed the consent of those they governed. The Empire’s elites—witnessing the disciplined legions, widespread religiosity, cultural efflorescence, and dominant economy—likely expected their world order to endure forever.”
“In the year 166 AD, however, seemingly eternal Rome was caught completely off-guard as a deadly novel disease swept across the Eurasian landmass. It ransacked Rome’s cities for at least a decade and preceded centuries of decline. This major biological event—now known as the Antonine plague—appears to have been the world’s first pandemic.”
“Chloropicrin and Its Alleged Use in the Ukrainian War”
JP Zanders breaks down the United States’ accusation that Russia used RCAs and chloropicrin against Ukrainian forces in this post on The Trench: “This three-part blog contribution analyses the publicly available information about RCA and chloropicrin use in the Russo-Ukrainian war. The first part summarises the chemical warfare allegations between 2014 and 2024. Part 2 investigates the reports of chloropicrin use, and the final part discusses how the international community can address the CW allegations through action in the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW).”
What We’re Listening To🎧
The Arms Control Poseur, The US and the Chemical Weapons Convention with Laura J. Gross
“On the ninth episode of season 2, William is joined by Laura J. Gross to discuss the completion of the destruction of the US chemical weapons stockpile.”
“In order to understand the current commitments of the United States to the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), Laura J. Gross joins William to discuss the completion of the destruction of the US chemical weapons stockpile, which was announced on the 7th of July 2023. This destruction was then verified by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW). In this episode, Ms Gross discusses the challenges that were faced in the destruction of this stockpile, and outlines the achievement itself in light of upholding global norms on arms control and verifiability. However, various challenges remain regarding the implementation of the Convention’s provision, such as the conflict in Gaza, the potential possession of chemical weapons by the Syrian Arab Republic, and the war in Ukraine. Ms Gross explains how the US assists other countries in the destruction of their declared chemical weapons stockpiles. When looking towards the future of the CWC, Ms Gross also touches upon the renewed use of chemical weapons by Syria, Russia, and North Korea and what the US is undertaking to counter the return to such use.”
“Laura J. Gross is the director of the Office of Chemical and Biological Weapons Affairs, Bureau of Arms Control, Deterrence, and Stability, at the United States Department of State, and she is the Executive Director of the US National Authority for the CWC.”
NEW-Pandemic Accord: Partial Failure or Partial Success?
From Brown Pandemic Center: “On 23 May at 12:00PM ET the Pandemic Center will host a webinar titled Pandemic Accord: Partial Failure or Partial Success?”
“Member States of the World Health Organization have been negotiating a new pandemic treaty to address challenges in the response to and sub-optimal international coordination during the Covid-19 pandemic. A vote on the treaty is expected during the upcoming World Health Assembly, taking place 27 May through 1 June. This Pandemic Center webinar will convene an expert panel to assess the strengths and limitations of the current draft of the treaty and its prospects for adoption.”
Learn more and RSVP here.
NEW-Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism
From TFAH: “Please join Trust for America’s Health (TFAH) for a virtual Congressional briefing and national webinar on our recent report, Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism.”
“The report identifies gaps in national and state preparedness to protect residents’ health during emergencies and makes recommendations to strengthen the nation’s public health system and improve emergency readiness. As the nation experiences an increasing number of infectious disease outbreaks and extreme weather events, the report found that while emergency preparedness has improved in some areas, policymakers not heeding the lessons of past emergencies, funding cuts, and health misinformation are all putting decades of progress at risk.”
“A panel of subject matter experts will discuss the nation’s readiness for public health emergencies, examine the findings of the report, and discuss key recommendations for policymakers. The briefing will include time for Q&A from the audience.”
This event will take place on May 29 and 2 pm EST. Learn more and register here.
NEW-Optimizing Federal, State, and Local Response to Public Health Emergencies
From NASEM: “The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine’s Committee on Science, Technology, and Law cordially invites you to attend a virtual workshop to examine how legal authorities affected the ability of public health agencies and federal, state, and local governments to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and explore approaches to ensure a more effective response to future public health crises. The allocation of legal authority has become an issue of immediate relevance as the United States confronts an H5N1 avian influenza outbreak in dairy cattle.”
“The workshop, which will highlight ideas for optimizing the response to future public health emergencies, will be held on Thursday, May 30, 2024 from 12:00 to 5:30 pm U.S. Eastern and Friday, May 31, 2024 from 12:00 to 4:30 pm U.S. Eastern. It will include the following sessions:
1) Optimizing Federal, State, and Local Public Health Preparedness
2) The COVID-19 Pandemic: What happened? What went right? What went wrong?
3) Public Health Emergency Authorities: What we know about them and how did we experience them before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Case Study I: Pandemic Orders and Religious Liberty
- Case Study II: New York City Vaccine Mandates: Who Has the Authority?
- Case Study III: The Experience with Public Health Emergency Authorities Before, During, and After COVID-19
- Case Study IV: The Future of Public Health Authority at the Federal, State, and Local Level
4) Exploring Routes and Barriers to Effective Public Health Response Efforts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
5) Looking to the Future: Where do we go from here?
6) Concluding Thoughts from Workshop Planning Committee”
Learn more and register here.
NEW-American Democracy and Health Security Initiative: Lighting a Path Amid Pandemic Polarization
“Please join the Brown University School of Public Health Pandemic Center, the COVID Collaborative, and the CSIS Bipartisan Alliance for Global Health Security for the launch of the American Democracy and Health Security Initiative.”
“The story of how America fared under the Covid-19 pandemic is actually two stories. While the more well-known story is one of failure, confusion, and polarization, the other story is one of American ingenuity amidst profound uncertainty. State and local leaders were at the center of this untold story—in serving their communities they innovated, bridged divides, and illuminated America’s path during the Covid-19 pandemic’s darkest days. The American Democracy and Health Security Initiative spotlights these lamplighters and harvests their hard-won lessons, to ensure the most successful strategies can be sustained or replicated in future crises.”
“On June 5, the American Democracy and Health Security Initiative will publish its findings on what actionable steps are needed to advance our health security for the future. The event will feature leaders from across the country from Governors, advisors, and health leaders to community organizations, educators, businesses, and crisis managers. We will discuss urgent opportunities to make the country more resilient against future threats to our health security and to our democracy and identify national and local innovations that must be retained and playbooks that are needed to reinvigorate leadership, bipartisanship, and equitable access in the face of the next health emergency in America.”
This event will take place on June 5 at 2 pm ET. Register here.
Getting Ahead of Avian Influenza: Why Organizations Need to Prepare Today
From Bluedot: “Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1), commonly referred to as bird flu, has been making headlines around the world, as the virus rapidly spreads to new animal species. Already the cause of a panzootic (global animal pandemic), last month a human H5N1 case was reported in the U.S. after likely contracting it from infected dairy cattle. The virus has now been detected in dairy herds across multiple states, with evidence to suggest it has been spreading more widely than previously thought — begging the question: Are we at risk for an avian influenza-instigated pandemic?”
“Join us for a deep dive into avian influenza as we explore why and how organizations should prepare to safeguard against bird flu. Together, through collaborative efforts and informed decision-making, we can mitigate the risk of increased transmission to humans. BlueDot’s experts have been closely monitoring the situation and potential risks, issuing multiple alerts on H5N1 — and other avian influenzas — over the past 15 months.”
This event will take place on May 23, at 11 am ET. Learn more and register here.
Addressing the Challenges Posed by Chemical and Biological Weapons: Intensive Online Introductory Course for Students of Technical Disciplines
“SIPRI and the European Union Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Consortium (EUNPDC) invite graduate and postgraduate students of the technical or natural science disciplines to apply for an intensive online introductory course on chemical and biological weapons—their proliferation, the efforts to eliminate them, the various mechanisms used to control their spread—and endeavours underway to reduce the risk of chemical or biological agents in terrorist attacks. The course will take place online, during four half-days on 28–31 May 2024, 14:00 to 18:00 Central European Summer Time (CEST).”
“The course will cover the fundamentals of chemical and biological weapons as well as of missiles and other means of delivery; the history of chemical and biological warfare; the evolution of international norms against these weapons; the threats associated with potential terrorist uses of chemical and biological material; bioweapons and other related scientific advances; the current challenges posed by chemical weapons; arms control treaties; and mechanisms to curb the spread of dangerous substances, including export controls.”
“The course will also discuss the role of the EU institutions and industry to address the challenges mentioned above. The course will be instructed by renowned experts on non-proliferation, arms control, disarmament, export controls, verification and related subjects from SIPRI, other European research centres, think tanks and international organizations.”
Learn more and apply here.
Registration for GHS 2024 Now Open
Registration is now open for the Global Health Security 2024 conference in Sydney, Australia. This iteration will take place 18-21 June, 2024. The call for abstracts is also still open. “The mission of the Global Health Security conference is to provide a forum where leaders, researchers, policy-makers, and representatives from government, international organisations, civil society, and private industry from around the world can engage with each other, review the latest research and policy innovations, and agree solutions for making the world safer and healthier. To that end, our mission is to help foster a genuinely multidisciplinary community of practice that is committed to working collaboratively to enhance global health security and eliminate disease, irrespective of its origin or source.”
SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology, and Biosecurity Conference in Africa
“Join us for the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa, a groundbreaking event that brings together experts, researchers, and enthusiasts in the field of synthetic biology. This in-person conference will take place at the Laico Regency Hotel from Wed, Jul 17, 2024 to Friday, Jul 19, 2024.”
“Get ready to dive into the exciting world of synthetic biology and explore its potential applications in Africa. From cutting-edge research to innovative solutions, this conference offers a unique opportunity to learn, network, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.”
“Discover the latest advancements, trends, and challenges in synthetic biology through engaging keynote speeches, interactive workshops, and thought-provoking panel discussions. Immerse yourself in a vibrant atmosphere where ideas flow freely and new connections are made.”
“Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in synthetic biology, this conference provides a platform to expand your knowledge, exchange ideas, and contribute to the growth of the field in Africa.”
“Don’t miss out on this extraordinary event that promises to shape the future of synthetic biology and biosecurity in Africa. Mark your calendars and join us at the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa!”
Learn more and register here.
IBBIS Announces The Common Mechanism
The International Biosecurity and Biosafety Initiative for Science (IBBIS) recently launched The Common Mechanism, “An open-source, globally available tool for DNA synthesis screening.” The organization explains on its website that “The Common Mechanism helps providers of synthetic DNA and RNA to effectively screen orders to prevent synthesis technology from being exploited. We provide free, distributed, open-source, automated software for screening sequences of nucleic acids (including DNA and RNA) as well as resources to facilitate customer screening.”
Learn more and access the tool here.

