Welcome to this week’s Pandora Report! 🍂 This issue features declining U.S. vaccination rates and early signs of a challenging flu season to the first human case of H5N5 avian influenza in Washington. We also cover international efforts to strengthen nucleic acid synthesis screening, debates over U.S. pandemic preparedness strategies, and insights from a new review of a state-level bioweapons programs in Russia and Iraq.
Important Note: The Pandora Report will be on break next week for Thanksgiving – wishing all our readers a happy and safe holiday ahead! 🍁🦃
Trust in U.S. Vaccines Falters as Measles and Flu Threaten a Harsh Winter Ahead
By Carmen Shaw, Co-Managing Editor of the Pandora Report

A series of developments this week suggests that the U.S. immunization landscape may be rapidly destabilizing. The CDC quietly revised its Autism and Vaccines webpage, softening language that previously stated that there is no link between vaccines and autism – despite decades of high-quality research debunking such claims. The shift has alarmed experts, who say it reflects what happens when politics hijack public health, further undermining trust in the agency. Others warn that any ambiguity on settled science risks renewed outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases in society. For many, the concern is not merely the change in wording but the broader signal it sends: federal health guidance is becoming less reliable and consistent at a moment when clarity is desperately needed.
This confusion is reflected in divergent vaccination behavior across the nation. Only 23% of U.S. adults have received this season’s COVID-19 vaccine, a dramatic drop from early pandemic levels (in early 2022, 75% of Americans had received at least one dose of the initial vaccine). The vaccination rates for flu, measles, and tetanus are also declining. Uptake varies sharply by region: the highest COVID-19 vaccination rates are found in the Northeast, including D.C., Vermont, Massachusetts, and Minnesota, while the lowest rates are observed in Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi. Public health researchers worry that vaccination rates may decline further, particularly among younger adults and Hispanic and Black Americans, who have lower vaccination rates, further exposing them to serious complications such as long COVID. These ongoing mixed messages from federal leadership and new access barriers in some Republican-led states are creating a fragmented and unpredictable vaccination environment. Although COVID may no longer dominate headlines as it once did, it still claimed more than 31,000 U.S. lives last year.
The consequences of declining trust in vaccines are already visible. A measles strain that ignited a major outbreak in the Southwest has now spread across the country, leading to 1,753 confirmed cases as of November 18 – more than six times the total reported in 2024, according to the CDC. Nearly all infections (92%) occur among people who are either unvaccinated or of unknown vaccination status. If transmission isn’t controlled soon, the United States is on track to lose its measles elimination status, mirror Canada’s recent loss of the designation just some days ago. Health officials frame the current moment bluntly: pockets of low vaccination are creating openings for opportunistic diseases Americans once assumed were gone.
These vulnerabilities are emerging just as the U.S. faces the prospect of a challenging flu season ahead. A mutated influenza strain, subclade K, is already driving early surges in the UK and Canada. U.S. scientists warn that this winter could bring a second consecutive severe flu season – last winter saw the highest rates of flu hospitalization in nearly 15 years, with at least 280 children dying from influenza, the highest pediatric death toll recorded since 2004. Now, with the new variant circulating, vaccination rates down, and holiday travel approaching, experts warn that a grim repeat is likely.
“The signs are, it could be a big season,” says Richard Webby, who studies the flu at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis. “The flu season might have a little bit of a punch to it this year.”
A new Pew Research Center poll adds another layer: while most Americans still believe childhood vaccines work in preventing serious illnesses, confidence among Republican voters continues to erode. As trust fractures along political lines, the nation’s ability to maintain stable immunization coverage becomes increasingly fragile.
Further Reading:
- “Trump and RFK Jr. are mulling their most disruptive vaccine policies yet — alarming manufacturers,” Daniel Payne, StatNews
- “How RFK Jr., America’s celebrity health secretary, is steamrolling,” Chelsea Cirruzzo, Casey Ross, and Sarah Todd, StatNews
- “Trump slashed spending on clinical trials. The toll is starting to become clear,” Allyson Chiu, Washington Post
Spotlight: Improving Pandemic Readiness with Michael Osterholm and GMU’s Gregory Koblentz – A Podcast
re we ready for the next pandemic? In Improving Pandemic Readiness, David Ramadan and guest co-host Gregory Koblentz, Director of GMU’s Biodefense Graduate Program, sit down alongside renowned epidemiologist Michael Osterholm, Director of CIDRAP and author of The Big One: How We Must Prepare for Future Deadly Pandemics. They discuss lessons learned from the COVID-19 response, including challenges with vaccine distribution and lockdown measures, and explore how young people can combat the pervasive spread of misinformation and disinformation.
Listen to the podcast here.
First Human Case of H5N5 Confirmed in Washington
By Margeaux Malone, Pandora Report Associate Editor
On November 14, Washington state health officials confirmed the first human case of H5N5 avian influenza in the United States, also marking the country’s first human bird flu case since February. The patient, reportedly an older adult with underlying health conditions, remains hospitalized after developing severe symptoms including high fever, confusion, and respiratory distress in early November. This represents the first known human infection with the H5N5 strain, distinct from the H5N1 strain that has affected thousands of cattle and poultry operations in recent months.
Investigators believe the patient was exposed through a mixed backyard flock of domestic poultry that had contact with wild birds. Health officials are monitoring close contacts but have identified no additional cases and do not believe there is yet increased risk to the public. Human-to-human transmission of avian flu has never been documented in the United States; however, the CDC continues to urge anyone who works with or may come into contact with potentially infected domestic or wild animals to take precautions including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and reporting sick or dead birds to the appropriate authorities as soon as possible. Although the majority of the confirmed U.S. human H5N1 cases have been mild, one Louisiana man died in January following infection with bird flu.
ProPublica Investigation Questions USDA’s Approach to Farm Outbreaks
A recently published ProPublica investigation has raised questions about the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) response strategy to bird flu, including the agency’s decision not to investigate potential airborne spread and its reluctance to authorize poultry vaccines despite calls from public health experts and the egg industry. The investigation examined a devastating bird flu outbreak last winter that began at a single Ohio facility and then spread to nearby farms, ultimately affecting over 20 million hens across 83 farms. Using genetic analysis, weather data, and wind simulations, ProPublica found that wind may be a plausible explanation for how the bird flu virus spreads between farms, as those downwind from the initial outbreak site were approximately 20 times more likely to develop infections.
The USDA has not investigated airborne transmission in this outbreak, garnering criticism from public health experts and industry leaders who argue that the current focus on wild birds and biosecurity alone has been insufficient to control the disease in light of the continuing bird flu outbreaks across the country. The investigation highlights that other countries have taken different approaches after documenting airborne spread through contaminated dust and feathers. For instance, France implemented poultry vaccination programs in 2023 following research showing the virus could travel on aerosols, leading to a near-total reduction in duck farm cases.
As the outbreak surges on into the fall migration season, public health experts and egg industry representatives urge the USDA to authorize poultry vaccines against avian influenza in the United States as well. Following a study showing the efficacy of poultry vaccines published in 2023, the USDA licensed a chicken vaccine against avian influenza developed by Zoetis in early 2025, raising hopes that nationwide vaccination programs may soon follow. However, U.S. vaccination efforts in poultry continue to face significant opposition from the chicken meat industry, which has been far less affected by bird flu but holds greater sway over the industry as a whole. These producers warn that vaccinating even egg-laying hens could trigger import bans from international trading partners. After France began its vaccination program, the United States paused all poultry imports from the European Union, citing worries that vaccines could mask infections by preventing symptomatic illness in birds. U.S. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins has stated that vaccine deployment is “at least a year or more away,” given concerns about “repercussions that we don’t fully understand.”
While the USDA appears to be committed to improving poultry farm biosecurity, pledging up to $500 million for farm audits and inspections, some experts told ProPublica they believe government leaders are stalling, hoping the virus will fizzle out on its own, just as it did a decade ago during the 2014-2015 H5N2 outbreak. Unfortunately, with 83 confirmed infected flocks in the last 30 days, more than double the number this time last year, the outbreak does not look like it will be slowing down any time soon.
Further Reading:
- “Rare Bird Flu Strain Detected in Washington State Resident,” Mandy Taheri, Newsweek
- “The Expected Cost of Your Thanksgiving Turkey in 2025,” Caitlinn Hubbell and Elijah Bryant, Purdue University College of Agriculture
- “Avian flu has decimated world’s largest breeding colony of southern elephant seals,” Mary Van Beusekom, CIDRAP
- “H5N1 bird flu cases are on the rise in Europe. How concerned should you be?” Ignacio López-Goñi, The Independent
- “Avian Influenza Fast Facts,” CNN Health
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Screening in Singapore
The Biodefense Graduate Program was out in force at a workshop held by the Engineering Biology Research Consortium (EBRC) in Singapore on November 4-5, 2025 to develop international best practices for screening sequences and customers to strengthen biosecurity. The goal of the workshop, one in a series being held by EBRC, is to build international consensus on best practices for the nucleic acid synthesis industry, focusing particularly on customer and sequence screening methods, and establish an informal global consortium of stakeholders representing industry, government, academia, and non-profit sector to advance the adoption and implementation of robust screening methods. Biodefense Program Director Dr. Gregory D. Koblentz, who is a member of EBRC’s Security Working Group, served as the discussant on a panel regarding the challenges and opportunities for achieving universal, aligned nucleic acid screening policy and practices. Dr. Koblentz highlighted weaknesses in both multilateral and national approaches to nucleic acid synthesis screening and advocated for a minilateral approach that would start with a small group of countries, companies, and other stakeholders who would establish rigorous screening standards and then work with other countries and companies to incentivize wider adoption of the standard. Two alumni from the Biodefense program also participated in the workshop. Henry Kim, Biodefense PhD ’20, who is currently a research fellow at the Institute for National Security Strategy, discussed South Korea’s interest in nucleic acid screening as a biosecurity tool. Andy Morgan, Biodefense Certificate ‘24, who is the Senior Policy Advisor for Biotechnology Policy & Regulation at the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment in New Zealand, discussed draft legislation on biotechnology innovation and regulation that would include nucleic acid synthesis screening.
Debating the U.S. Pandemic Preparedness Playbook: Risks, Reality, and Rebuttals
Two sharply contrasting perspectives on pandemic preparedness dominated discourse last week. In City Journal, NIH Director Jay Bhattacharya and his Principal Deputy Director Matthew J. Memoli published an essay, arguing that the U.S. should create a dramatically revised “pandemic preparedness playbook.” They described it as a three-step agenda:
- Catalog every existing pathogen by sending scientists to remote areas around the world.
- Evaluate the risk of each pathogen infecting humans by testing its ability to penetrate human cells – a step they characterize as potentially involving genetic modification in a practice now called dangerous gain-of-function research (dGOF).
- Develop and stockpile countermeasures such as vaccines and therapeutics in advance of future spillover events.
Bhattacharya and Memoli portray this approach as inherently risky and suggest that past U.S. preparedness investments failed or even contributed to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In response, Jeremy Faust, writing for Inside Medicine, published a rebuttal, criticizing the essay for misrepresenting both the scientific record and the purpose of U.S. preparedness programs. Faust – citing virologist Angela Rasmussen and others – counters that decades of NIH-funded coronavirus and mRNA research made the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines possible and saved millions of lives. He notes that wildlife surveillance and lab characterization are standard, tightly overseen scientific practices, not reckless attempts to “create” threats. They also emphasize that the weight of peer-reviewed evidence supports a zoonotic origin of SARS-CoV-2 linked to wildlife trade at the Huanan Wholesale Seafood Market in Wuhan – not laboratory work – and warns that abandoning scientific consensus for ideological narratives would leave the U.S. less, not more, prepared for the next pandemic.
Further Reading:
- “The pandemic next time,” Jon Cohen, Science
- “Where Do Viruses Come From?” Kamal Nahas, The Scientist
- “COVID vaccine rollout and pandemic preparedness assessed in new book, ‘Fair Doses,’” Jonathan Lambert, NPR
- “What Would Happen To Americans In A Bird Flu Pandemic?” Stephanie Psaki and Beth Cameron, Health Affairs
- “National Institutes of Health staffer put on nondisciplinary leave after criticizing NIH politicization,” Joseph Choi, The Hill
- “NIH Job Postings Raise Red Flags for Scientists,” Kristina Fiore, MedPage Today
New Review Article: How States Build Bioweapons: Lessons from Russia and Iraq
In a new review, Amy E. Smithson examines how political leadership, institutional culture, and strategic doctrine shaped the Soviet/Russian and Iraqi illicit bioweapons programs. It analyzes each program’s motivations, organizational structure, scientific capacity, biosafety practices, and operational visibility – highlighting how these sociopolitical factors influenced agent selection, R&D, and military planning. By contrasting the two cases, the study draws lessons on how such contextual signals can help analysts better detect clandestine bioweapons efforts and anticipate proliferation risks.
In Other News
US and Global Health Policy, Funding Cuts and Governance
- “Brazil Wins Limited Backing for COP30 Climate-Health Plan, But Nations Commit No Finance,” Stefan Anderson, Health Policy Watch
- “Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths by 2030, study warns,” FRANCE 24
- “UK warned that 15% cut to health fund will force ‘impossible choices’ on Africa,” Kat Lay, The Guardian
- “U.S. Congress considers sweeping ban on Chinese collaborations,” Jeffrey Mervis, Science
- “China’s Grip on American Medicine Cabinets Grows More Entrenched,” Anna Edney, Bloomberg
Global Infectious Disease Outbreaks
- “Ethiopia faces its first Marburg outbreak, which has proved deadly,” Stephanie Soucheray, CIDRAP
- “Ethiopia reports three Marburg deaths, declares no active cases,” Addis Standard
- “Ethiopia reports first outbreak of Marburg, Ebola cousin with no vaccine,” Robi Raji, Washington Post
- “The next pandemic is already here: Antimicrobial resistance is upending a century of achievements in global health,” WHO
Biosecurity, Biothreats, Militarization, and Biological Risks
- “Legitimate Research or Biological Threat? Detecting Misuse of the Biological Supply Network and Policy Options to Reduce Risks,” RAND
- “Secret U.S. Memo Authorizing Drug-Boat Strikes Cites Chemical Weapon Threat,” Alexander Ward, Lara Seligman, and Michael R. Gordon, The Wall Street Journal
- “Chinese National Pleads Guilty and is Sentenced for Smuggling a Dangerous Biological Pathogen into the U.S. While Working at a University of Michigan Laboratory,” United States Attorney’s Office
- “Chinese scientist charged with smuggling pathogen into US to be deported,” The Guardian
- “OpenAI backs startup aiming to block AI-enabled bioweapons,” Deepa Seetharaman, Reuters
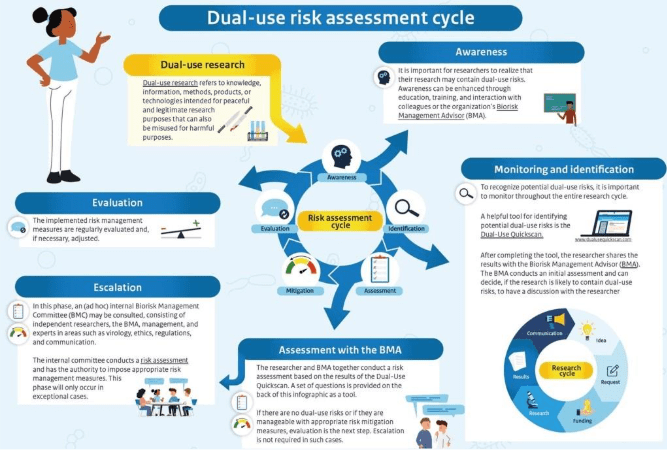
How Can the Biological Weapons Convention Address the Dual-Use Challenges of AI-Driven Biodesign Tools?
From UNIDIR: “In collaboration with the Biological Weapons Convention Implementation Support Unit (BWC-ISU) at the United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs (UNODA), UNIDIR is organizing a series of online technical briefs on emerging technologies and the BWC. The upcoming session will focus on artificial intelligence (AI) enabled tools for molecular design and biological engineering – areas advancing at a rapid pace. It will examine their current capabilities, potential dual-use risks, evolving international policy responses, and implications for strengthening the BWC. The session will include a conversation-style expert panel, followed by an interactive question-and-answer segment with the audience.”
This event will take place online on November 26, 2025. Learn more and RSVP here.
Cyberbiosecurity: Emerging Risks and Opportunities for the Biological Weapons Convention
From UNIDIR: This session is organized as part of UNIDIR’s “Science and Technology Watchtower” project, aimed at identifying science and technology (S&T) developments and analysing their risks and opportunities for disarmament and international security. It will feature a short presentation of the main findings of UNIDIR’s new paper Cyberbiosecurity: A Matter of International Peace and Security?. The session will then feature a conversation-style panel with experts to explore the implications of cyberbiosecurity for bioscience governance, verification, and national implementation of the BWC, followed by a question-and-answer session with the audience.”
This event will take place online on December 4, 2025. Learn more and RSVP here.
GHS 2026
From GHS: “We’re excited to officially announce that the 4th Global Health Security Conference (GHS2026) will be held in Kuala Lumpur on the 9 – 12 June, 2026!”
“Building on the incredible momentum of GHS2024 in Sydney, we look forward to bringing together the global health security community once again – this time in one of Southeast Asia’s most vibrant and dynamic cities.”
“Registration and Call for Abstracts are now live!”
Learn more, submit abstracts, and register here.
NEW: Call for Experts: Forum on Medical and Public Health Preparedness for Disasters and Emergencies
From NASEM: “The National Academies is seeking suggestions for experts to be considered to fill 5 to 7 open seats on the Forum on Medical and Public Health Preparedness for Disasters and Emergencies. The forum fosters in-depth discussion and collaboration to examine barriers, identify research, explore innovative operational and policy solutions, and inspire action among diverse stakeholders in support of sustaining and advancing national health readiness and security. Additionally, staff are identifying potential speakers, participants, and other contributors for upcoming forum activities.”
Submit your nominations by December 8 here.
NEW: African Atomic Voices Network (AAVN)
From AAVN: “The African Atomic Voices Network (AAVN) is a collaborative, career-development community for young professionals, students, and researchers from Africa (aged 18–35) who are working in, or passionate about, nuclear issues and related global security challenges such as artificial intelligence, emerging technologies, and chemical & biological security. The Network empowers African young professionals to shape global conversations and ensures that Africa’s voice is amplified in nuclear and broader global security discourse.”
Learn more and join the network here.
NEW: CNS Young Women in Nonproliferation Initiative
From the initiative: “Established in 2018, the CNS Young Women in Nonproliferation Initiative aims to encourage undergraduate women to consider careers in WMD nonproliferation, arms control, and disarmament. As part of this initiative, we offer a mentorship program that enables undergraduate women to work directly with leading experts in their areas of professional interest.”
Learn more and join the network here.
Cyberbiosecurity Quarterly Call for Papers
“We are pleased to announce the launch of Cyberbiosecurity Quarterly, a new academic and trade journal dedicated to the intersection of cybersecurity and the bioeconomy. Published by Kansas State University’s New Prairie Press and sponsored by the Bioeconomy Information Sharing and Analysis Center (BIO-ISAC), this quarterly journal will serve as an important resource for professionals, researchers, and policymakers working to safeguard digital and physical biological infrastructures. Cyberbiosecurity is an emerging discipline that addresses the protection of biomanufacturing, biomedical research, synthetic biology, digital agriculture, and other life sciences sectors from digital threats. This journal will explore topics at the nexus of cybersecurity, digital biosecurity, and the bioeconomy, including but not limited to:
- Best practices for network configuration and management in biomedical environments (ingress/egress protection, segmentation, isolation, access control, traffic protection, etc.)
- Cybersecurity Vendor Management and Assessment
- Cyber and Digital Biosecurity Education for the Bioeconomy’s Workforce
- The Quality-Cybersecurity Tension in Practice and Techniques for Mitigation
- Threat Intelligence for Cyber-Physical Biological Systems
- Regulatory and Policy Perspectives on Cyberbiosecurity
- Incident Response and Risk Mitigation in Biomanufacturing
- AI and Machine Learning in Digital and Cyber Biosecurity”
Learn more and submit your papers here.
Harvard LEAD Fellowship for Promoting Women in Global Health
From Harvard’s Global Health Institute: “To equip and empower more leaders in global health, the Harvard Global Health Institute, in collaboration with the Department of Global Health and Population at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, offers a transformational 1-year fellowship specifically designed to promote leadership skills in individuals in low- and middle-income countries who will, in turn, mentor future female leaders in global health. Candidates should be currently based/working in a LMIC, and plan to return there after their fellowship.
The fellowship experience provides global health leaders time to reflect, recalibrate, and explore uncharted territories. To date, fellows have come from 18 different countries, with representation from Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and South America. Their areas of focus have ranged from HIV/AIDS and healthcare to health policy at the highest levels of government. Past fellows’ areas of expertise span disciplines including research, advocacy, administration, and policy.”
Learn more and submit your application by November 30 here.
Call for Presenters: International Bio Recovery Summit
The American Bio Recovery Association (ABRA) has opened its Call for Presenters for the 2026 International Bio Recovery Summit, taking place March 16-18 in Aberdeen, Maryland. As the industry’s leading event, the summit brings together bio-recovery professionals to address emerging challenges, regulatory updates, new technologies, and evolving safety standards in the field. ABRA invites experts to submit proposals aligned with conference objectives – including discussions on industry guidelines, insurance claims, hazardous substances, and business practices.
Learn more and submit your presentation by December 31 here.
64th ISODARCO Course
From ISODARCO: “In recent years, the global security landscape has become increasingly volatile, shaped by a convergence of geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and evolving nuclear doctrines. The post-Cold War order that once provided a measure of predictability in global security has eroded. Conflicts such as the wars in Ukraine and Gaza, rising tensions in the Indo-Pacific, and strategic competition between major powers have reshaped alliances and strategic postures.”
“At the same time, disruptive technologies including artificial intelligence, quantum computing, hypersonic missiles, and cyber threats – are adding new layers of complexity to both nuclear and conventional deterrence dynamics. These technologies are not only distorting the information landscape but also compressing decision-making timelines and complicating signaling mechanisms, increasing the risk of miscalculation.”
“Effectively managing nuclear escalation risks in this environment will require a combination of innovative diplomacy, technological safeguards, and renewed dialogue mechanisms to rebuild trust, reduce misperceptions, and stabilize strategic relations.”
“The ISODARCO 2026 Winter Course presents an invaluable opportunity for students and experts to discuss and examine these dynamics in depth and explore approaches to re-establishing strategic stability and reducing nuclear dangers in a volatile world.”
This course will take place January 11-18, 2026, in Andalo. Learn more and apply here.