Happy Friday! This week’s edition of the Pandora Report covers Volodymyr Zelenskyy’s warning about Russia’s continued occupation of Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant on the 38th anniversary of the fateful explosion at Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, updates on the federal government’s sluggish response amid continued spread of H5N1 in the United States, and more.
On Chornobyl Disaster Anniversary, Zelensky Warns Russian Seizure of Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant Could Lead to Similar Disaster
Today, on International Chernobyl Disaster Remembrance Day and the 38th anniversary of the explosion at Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy highlighted the ongoing risk posed by Russia’s occupation of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant. Russia has occupied the plant since March 2022, and it briefly held the site in Chornobyl earlier in its invasion. Both incidents have sparked concern due to unsafe practices at both locations.
In his statement, Zelenskyy said “Radiation sees no borders or national flags. The Chornobyl disaster demonstrated how rapidly deadly threats can emerge. Tens of thousands of people mitigated the Chornobyl disaster at the cost of their own health and lives, eliminating its terrible consequences in 1986 and the years after…For 785 days now, Russian terrorists have held hostage the Zaporizhzhia NPP. And it is the entire world’s responsibility to put pressure on Russia to ensure that ZNPP is liberated and returned to full Ukrainian control, as well as that all Ukrainian nuclear facilities are protected from Russian strikes. This is the only way to prevent new radiation disasters, which the Russian occupiers’ presence at ZNPP constantly threatens.”
As of March this year, “The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) board of governors resolution notes that the six-unit Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant (ZNPP) has been under Russian military control for more than two years and “expresses serious concern about the unstable state of nuclear safety and security at the ZNPP, especially the lack of adequately qualified personnel at the site, gaps in planning and prevention work, the lack of reliable supply chains, the vulnerable state of water and electricity supply outside the site, as well as the installation of anti-personnel mines in the buffer zone between the internal and external perimeter of the installation”.” (World Nuclear News)
Another Game of Infectious Disease Chicken? Federal Government Under Scrutiny for Slow H5N1 Response
Veterinarians and other professionals in the United States and abroad are increasingly criticizing the federal government for what they describe as a delayed effort to share data on viral changes, spread, and milk safety as H5N1 continues to spread in several states. So far, 33 dairy cattle herds in eight states have tested positive. Following the announcement of a human case in Texas recently, concern among scientists and the general public has continued to grow, though authorities continue to emphasize the US milk supply is safe and the risk to the general public is low.
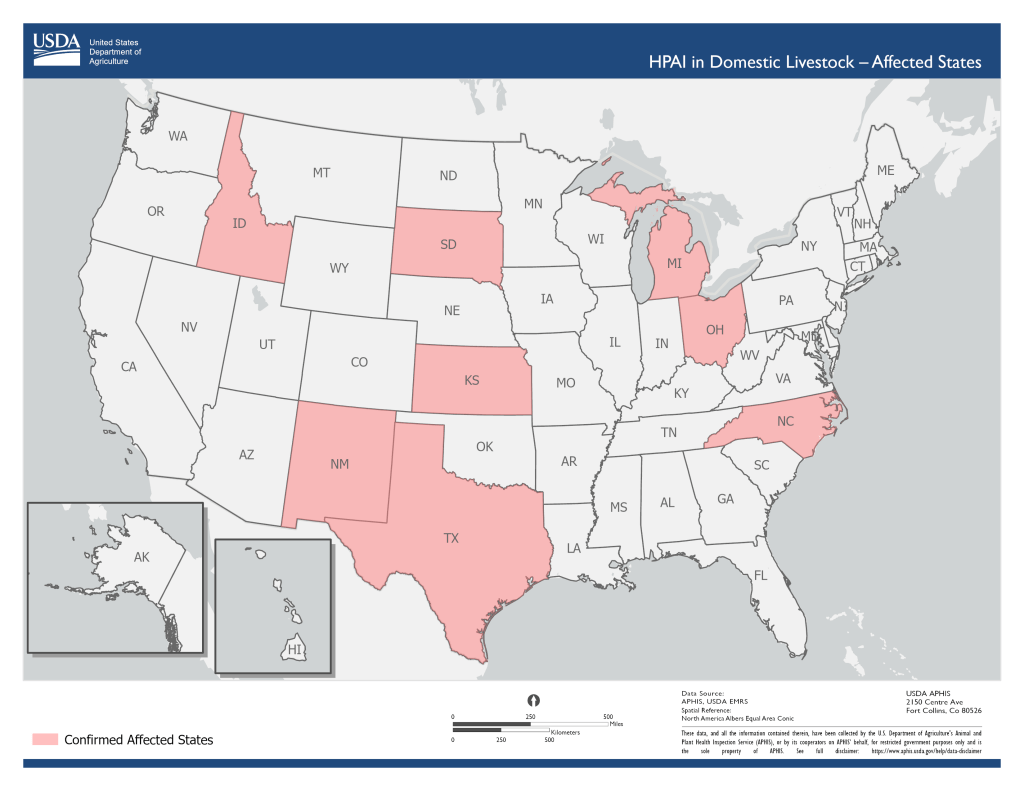
However, 1 in 5 retail milk samples in the country now test positive for H5N1 fragments according to the FDA, leaving some even more weary. This comes as the Department of Agriculture recently announced that there is growing evidence the virus is spreading among cows, in addition to continued spread from birds to cows. Furthermore, officials in North Carolina have reported a herd tested positive while remaining asymptomatic, though USDA has yet to discuss this publicly. The USDA is currently not requiring farms to test their herds for infection, though it did announce it will begin reimbursing farms for testing cows that are not symptomatic in addition to those that are visibly ill.
As STAT News explains, “Three and a half weeks after first announcing the startling news that cows from a milking herd in Texas had tested positive for H5N1, the government agencies involved in the investigations have not yet revealed what research shows about whether pasteurization of milk kills this specific virus. And until Thursday, U.S. officials had not disclosed whether the now 29 affected herds in eight states form a single linked outbreak fueled by the movement of cattle from the Texas panhandle, where the first outbreak was discovered. At present, STAT was told, that does not appear to be the case.”
The same article continues: “Other countries are trying to determine whether this event is a strange one-off, or proof that the wily virus has evolved to be able to infect cattle more easily, and what risk their own herds — and potentially people — could face if the latter is true. But they are operating largely in the dark because the United States has released such sparse information, said Marion Koopmans, head of the department of viroscience at Erasmus Medical Center in the Dutch city of Rotterdam.”
As this all points to the outbreak being larger than previously thought, the USDA has implemented a rule requiring the testing of all lactating cows before they can be moved across state lines, though experts think this is probably not going to do much to contain transmission at this point. There have also yet to be cases in pigs, which is good because pigs have human and avian receptors, making them especially dangerous in the context of H5N1 spread. However, the US government’s slow reaction and hesitancy to share information is deeply concerning for several key reasons.
A lack of transparency now holds the potential to be incredibly damaging if H5N1 spreads much further, particularly if it does begin spreading in pigs or person-to-person. While the US government does have stockpiled antivirals and vaccines that should be effective against this virus, depending on these measures and continuing to act as if everything is fine is a very dangerous game. Public trust in relevant institutions and these tools is at a dangerous low, and the public is likely to be more susceptible to mis- and disinformation if the federal government continues to drag its feet on sharing information now. This is a major threat to global health, and action needs to be taken now to give everyone, not just the US, the best chance to respond appropriately if this problem does escalate.
Donna E. Shalala Named Co-Chair of Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense
Former Secretary of Health and Human Services Donna E. Shalala was named Co-Chair of the Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense this week following the passing of former Senator Joe Lieberman, a founding Co-Chair of the Commission, last month. She will serve alongside former Pennsylvania Governor and DHS Secretary Tom Ridge. The Commission’s announcement explains that “Dr. Shalala is Trustee Professor of Political Science and Health Policy at the University of Miami, where she served as president from 2001-2015. She served in the U.S. House of Representatives from 2018-2020, representing Florida’s 27th Congressional District. In 1993, President Clinton nominated her as Secretary for Health and Human Services, where she served for eight years. Most recently, Dr. Shalala was named interim president of The New School in New York City.”
‘“This issue of biodefense, of keeping us safe from biological weapons and pandemic-causing diseases, was of great importance to Joe as it is to each of us who continue this work,” said Dr. Shalala. “I thank Gov. Ridge for his steadfast leadership, and for welcoming me as his co-chair.”’
Michael Koeris Appointed Director of DARPA’s Biotechnologies Office
Michael Koeris, Professor of Bioprocessing and a member of the Amgen Bioprocessing Center at the Keck Graduate Institute, was recently tapped to lead the Defense Advanced Research Agency (DARPA) Biotechnology Office (BTO). Koeris has been influential in the field of synthetic biology for years, having recently led the NIH’s RADx initiative as a portfolio executive and serving as Senior Bio Advisor & Venture Partner to The Venture Collective. In this new role, Koeris will oversee DARPA’s efforts to prioritize advancements in synthetic biology, particularly as it relates to areas like AI and space.
Read more about Koeris’ background and path to DARPA’s BTO here.

“Reinforcing Global Biodefense: The Case for Amending the Biological Weapons Convention to Enhance International Law and Legitimacy”
Biodefense PhD Student Ryan Houser recently published this article in the Rutgers Law Record, explaining in his introduction “The BWC is the cornerstone of the biological weapons disarmament regime, but the treaty is having difficulty keeping up with changing threats due to its decision-making process and geopolitics. Fundamentally flawed, the BWC is “crippled by key compromises made by the great powers in pursuit of various self interested security objectives in the context of the Cold War.”5 In November 2022, over two years after the widescale emergence of COVID-19, the international community met to review the BWC for the ninth time. In early 2022, the prospects for strengthening the BWC were the best they had been in years as China, Russia, and the United States had articulated individual plans that reflected enough common ground to craft a workable compromise.6 This cautious optimism around the BWC’s improvement prospects were spoiled by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February of 2022. The illegal aggression of Russia undermined the rules-based international order that the BWC is intertwined with. As part of the invasion, Russia also deliberately fabricated allegations levied against Ukraine, the United States, and other partners7 which “stigmatizes and politicizes biosafety, biosecurity, and cooperative public health and life sciences research to the detriment of not just Ukraine, but global health security overall.”8 Efforts to misrepresent or undermine legitimate biosafety and biosecurity research and capacity building weaken the BWC and undermine international cooperation for peaceful purposes.”
“Bringing New Technologies to Bear for Biosurveillance”
Biodefense PhD program alumnus and Schar School adjunct faculty member Daniel M. Gerstein recently coauthored this piece for Food Safety Magazine, which explains in its introduction “Public health, agriculture, the environment, and the food supply could be severely affected by the presence of infectious agents that occur naturally, are the result of accidents, or are intentionally introduced. Yet today, the capability to detect these biological pathogens effectively and rapidly is lacking. This shortfall continues, despite recent key technological advances that could alter the biosurveillance landscape…The foundations of biosurveillance lie in the One Health concept, which the World Health Organization defines as “an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimize the health of people, animals, and ecosystems.”1 This approach acknowledges the direct relationship between the health outcomes of people, animals, and ecosystems. What affects one, affects all.”
“Teetering on the Edge: Retaliatory Strikes Between Iran and Israel”
Schar School faculty member Mahmut Cengiz recently published this article with Homeland Security Today, writing in his introduction “Once again, tensions are rising in the Middle East, and the continuous cycle of retaliatory strikes between Iran and Israel could lead to unintended consequences and jeopardize security in the region. The Hamas terrorist attacks on October 7, 2023, marked a significant turning point in the history of terrorism and its impact on regional dynamics in the Middle East. These attacks resulted in the deaths of more than 1,300 Israelis, prompting severe retaliatory measures from Israeli forces. However, Israel’s counterterrorism efforts have faced strong criticism due to the casualties of over 33,000 Palestinians and the destruction of thousands of buildings in Gaza. The disproportionate number of civilian casualties, particularly women and children, has sparked debate regarding the legitimacy of terrorist operations in the region. The Tehran regime has promptly engaged in the conflict to pursue regional and global opportunities.”
“Statement of the G7 Non-Proliferation Directors Group, G7 Italy 2024”
The G7 Non-Proliferation Directors Group recently released their statement ahead of the G7 meeting in Italy this June. Their statement covers numerous areas, including nuclear safeguards, conventional weapons, AI and emerging technologies, and more. On biological and chemical weapons, they explain in part “The G7 reaffirms its strongest commitment to effective multilateral actions against the proliferation of all weapons of mass destruction and their means of delivery. As such, we continue to stress the centrality of the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) and the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BTWC), and the importance of ensuring their full and effective implementation and universalization.”
Read the entire statement here.
“Strengthening Global Biosecurity and Biosafety Efforts: The Role of the BWC National Implementation Database in Informing and Guiding National Policies”
Jaroslav Krasny recently authored this blog post for the National University of Singapore’s Centre for International Law, explaining in part “The Biological Weapons Convention National Implementation Database (“BWC Database”), developed collaboratively by the United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR) and the Verification Research, Training and Information Centre or VERTIC, serves as a resource for understanding and supporting the implementation of the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC). This new database compiles information on how State Parties meet their obligations under the BWC. It is designed to assist a wide range of stakeholders, such as government officials, legal professionals, researchers, non-governmental organizations, international bodies, and the private sector, by providing access to detailed information on national implementation practices. The objective is to support compliance with the BWC and contribute to global efforts in biosecurity and biosafety by making relevant information accessible to all interested parties.”
“NTI Convenes the First International AI-bio Forum”
From the Nuclear Threat Initiative: “NTI | bio convened more than 25 high-level biosecurity professionals, AI experts, and policymakers for the inaugural meeting of the International AI-Bio Forum. Participants included representatives from industry, such as Anthropic and Google DeepMind, experts from China, India, Nigeria, the U.K., the U.S., and representatives from multilateral institutions. The virtual meeting was held on April 10-11 and focused on defining the scope, institutional structure, and initial priorities of the International AI-Bio Forum to position it for success in reducing risks associated with rapidly advancing AI-enabled capabilities to engineering living systems.”
Read more here.
“Fighting ‘Smart’ Pandemics: Mitigating Risks and Harnessing the Potential of AI for Biosecurity”
This report was produced by Foreign Policy Analytics with support from the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI): “Each year, FP Analytics (FPA) invites practitioners, experts, and thought leaders to participate in interactive, scenario-based simulations that foster dialogue and seek innovative solutions to pressing global issues. In February 2024, FPA partnered with the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) and the Munich Security Conference (MSC) to produce a simulation, “Fighting ‘Smart’ Pandemics.” The simulation built upon a multistakeholder roundtable discussion that FPA and CEPI co-hosted on the sidelines of the 2023 UN General Assembly, which highlighted the intersection of AI and biosecurity as a key priority area warranting deeper and sustained engagement from global leaders. CEPI, alongside the International Pandemic Preparedness Secretariat, has led a “100 Days Mission” to enable the design, testing, and development of pandemic countermeasures within 100 days of an epidemic or pandemic threat’s emergence, a goal supported by the G7 but not yet realized.”
“A National Security Insider Does the Math on the Dangers of AI”
This Wired piece covers an interview with Jason Matheny, CEO of the RAND Corporation, and his thoughts on AI advancement making it easier to create biological and other weapons. In it, he explains his transition from working in public health to focusing on national security and how this has shaped his thinking, saying in part “When I first started getting interested in biosecurity in 2002, it cost many millions of dollars to construct a poliovirus, a very, very small virus. It would’ve cost close to $1 billion to synthesize a pox virus, a very large virus. Today, the cost is less than $100,000, so it’s a 10,000-fold decrease over that period. Meanwhile, vaccines have actually tripled in cost over that period. The defense-offense asymmetry is moving in the wrong direction.”
“Strengthening Biosecurity in Southeast Asia”
DTRA’s Andrea Chaney recently authored this piece that covers the recently-concluded Southeast Asia Strategic Biosecurity Dialogue. She explains in part, “In the context of Southeast Asia’s increasingly complex biosecurity landscape, dialogue participants engaged in several roundtable discussions covering a range of biosafety and biosecurity topics. Participants brought a broad scope of expertise, including health, defense and law enforcement, biology and biotechnology, international relations, and non-proliferation. The discussions encompassed Southeast Asia’s regional biosecurity priorities; building resilience to future threats; laboratory biosecurity and biosafety; the convergence of biology and emerging technologies; medical countermeasures development, production, and stockpiling strategies; and the role of the military in biosecurity.”
“Emerging Biotechnology Capacity and Emerging Biosecurity Threats in Colombia and Chile”
Steve S. Sin recently published this section in a report from the Army War College, “Emerging Technologies and Terrorism: An American Perspective”: “With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, countries around the world came to recognize the importance of maintaining a national stockpile of biologics (for example, vaccines) and, if possible, possessing domestic capabilities to produce the biologics required to fight the spread of communicable diseases. In South America, Colombia and Chile at one point possessed robust vaccine production capabilities but abandoned them decades ago.1 Although some within these countries called for a renewal of their vaccine production capabilities, the calls went unheard—that is, until the COVID-19 pandemic. As the world weathered the pandemic and countries scrambled to secure the vaccines needed to combat it, Colombia and Chile decided they would return to producing biologics domestically as well as double down on their already-active biotechnology policies that had been designed to encourage public-private partnerships and attract foreign investments.”
“Biotech Matters: Public-Private Coordination of Biotechnology”
Richard Danzig recently authored this piece for CNAS, writing in part “The U.S. successes and failings during the COVID-19 pandemic, combined with perceptions that China vigorously coordinates its public and private sectors, generated calls for an American industrial policy that would further orchestrate biotechnology work in the United States. In this context, the natural tendency is to regard improved coordination as straightforwardly achievable through improved processes and enlightened leadership…The nation would be well advised, however, to recognize that the difficulties are more deeply rooted than simply failures of will, imagination, or efficiency. Three deep-seated problems impede progress.”
APIC Emerging Infectious Diseases HPAI Playbook
The Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology regularly publishes playbooks for specific diseases, including a new one for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: “To help infection preventionists quickly activate Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) prevention efforts, APIC’s Emerging Infectious Diseases Task Force has created an HPAI Playbook that IPs can download and customize for use in their facilities. The Playbook is a concise workflow document that is designed to be user-friendly and operational for busy IPs.”
“The Viral Most Wanted: The Hantaviruses”
CEPI’s Kate Kelland recently authored this latest entry in CEPI’s Viral Most Wanted focused on the hantaviruses, writing in the work’s introduction: “The Albuquerque Journal, a newspaper in the U.S. state of New Mexico, ran an alarming headline in its May 27th edition in 1993: “MYSTERY FLU KILLS 6 IN TRIBAL AREA”. The article told a story that had first come to light two weeks earlier, when a 19-year-old man was rushed to the emergency department of the Indian Medical Centre in Gallup.”
“The man, a Native American from the Navajo tribe, had been travelling with his family to his fiancée’s funeral when he began struggling to breathe in the car’s back seat. The family veered off the road to call for an ambulance. Both the first responders and, later, the emergency room doctors tried to revive the victim with cardiopulmonary resuscitation, but their efforts were in vain. The young man’s lungs were flooded with fluid. He had effectively drowned.”
“The ER doctors were shocked, not only at the speed and dramatic nature of the man’s death, but by the similarity of the case to that of a young woman a few weeks earlier who had suffered the same symptoms and also died.”
“Over the next few weeks, more than a dozen more people in the area contracted the deadly disease, many of them young Navajos.”
“During the same period, doctors and public health officials tried desperately to identify what was causing the outbreak. On June 11th, 1993, the weekly Morbidity And Mortality report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Prevention and Control (CDC) revealed that the mystery pathogen was “a previously unrecognized Hantavirus”.”
“The novel viral villain belonged to the Hantavirus family—a group of viruses normally carried by rats, mice and other rodents and known to cause severe disease in people. The Hantavirus family is one of The Viral Most Wanted.“
“Public Health Preparedness: Mpox Response Highlights Need for HHS to Address Recurring Challenges”
The Government Accountability Office recently published this report on HHS’ response to the mpox outbreak in the United States: “Health and Human Services was initially charged with coordinating the federal response to a 2022 global outbreak of mpox—a smallpox-related virus.”
“State and local jurisdictions cited challenges in the federal response such as difficulty accessing and using vaccines and tests, which may have led to unnecessary suffering. We added HHS’s leadership and coordination of public health emergencies to our High Risk List earlier in 2022 due to similar issues in past responses.”
“We recommended that HHS adopt a coordinated, department-wide program that incorporates input from external stakeholders to identify and resolve challenges.”
“Deadly Diseases and Inflatable Suits: How I Found My Niche in Virology Research”
Nikki Forrester recently authored this spotlight piece for Nature covering the career of Hulda Jónsdóttir: “Virologist Hulda Jónsdóttir studies some of the world’s most pathogenic viruses at the Spiez Laboratory in Spiez, Switzerland. For her, highly pathogenic viruses are more often a source of curiosity than of concern. Jónsdóttir, who runs a research group at the Spiez Laboratory, regularly dons a giant, inflatable protective suit to research disinfectants and antiviral compounds to combat several lethal viruses, including Ebola virus and Lassa virus. Jónsdóttir spoke to Nature about carving her own path in virology research and why she chose to pursue a career in Switzerland and at the Spiez Laboratory, which is owned and funded by the Swiss government.”
What We’re Watching 🍿
IR Thinker, Chemical and Biological Weapons – Brett Edwards | 2024 Episode 7
“In this enlightening interview, Dr. Brett Edwards, an expert in chemical and biological weapons, describes the history, current capabilities, and future challenges associated with these formidable weapons systems. Dr. Edwards discusses the evolution of chemical and biological warfare, the verification processes for weapon destruction, and how these weapons integrate into national military strategies. He also addresses the ethical debates surrounding their use, international efforts to control such weapons, and the specific challenges posed by conflicts like the ongoing war in Ukraine.”
Watch here.
ICYMI-Oppenheimer: The Rest of the Story
Middlebury’s James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies recently hosted this event with Siegfried Hecker: “Christopher Nolan’s biopic Oppenheimer has captured the interest of nearly 100 million people around the world. Dr. Hecker will provide the back story to some key elements of the film and share his views on the legacy of Oppenheimer and the Manhattan Project, based on his more than five-decades associated with the laboratory Oppenheimer led.”
The event recording is available here.
3rd International Biosecurity Virtual Symposium
From ABSA: “The Symposium will bring together biosecurity professionals from a wide range of disciplines with varying expertise to share their experiences and knowledge on diverse biosecurity topics. The Symposium will offer attendees an opportunity to learn the latest in biosecurity and have thought-provoking conversations about real-world biosecurity issues, concerns, and scenarios.”
This symposium will take place May 7-8. Learn more and register here.
Addressing the Challenges Posed by Chemical and Biological Weapons: Intensive Online Introductory Course for Students of Technical Disciplines
“SIPRI and the European Union Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Consortium (EUNPDC) invite graduate and postgraduate students of the technical or natural science disciplines to apply for an intensive online introductory course on chemical and biological weapons—their proliferation, the efforts to eliminate them, the various mechanisms used to control their spread—and endeavours underway to reduce the risk of chemical or biological agents in terrorist attacks. The course will take place online, during four half-days on 28–31 May 2024, 14:00 to 18:00 Central European Summer Time (CEST).”
“The course will cover the fundamentals of chemical and biological weapons as well as of missiles and other means of delivery; the history of chemical and biological warfare; the evolution of international norms against these weapons; the threats associated with potential terrorist uses of chemical and biological material; bioweapons and other related scientific advances; the current challenges posed by chemical weapons; arms control treaties; and mechanisms to curb the spread of dangerous substances, including export controls.”
“The course will also discuss the role of the EU institutions and industry to address the challenges mentioned above. The course will be instructed by renowned experts on non-proliferation, arms control, disarmament, export controls, verification and related subjects from SIPRI, other European research centres, think tanks and international organizations.”
Learn more and apply here.
Registration for GHS 2024 Now Open
Registration is now open for the Global Health Security 2024 conference in Sydney, Australia. This iteration will take place 18-21 June, 2024. The call for abstracts is also still open. “The mission of the Global Health Security conference is to provide a forum where leaders, researchers, policy-makers, and representatives from government, international organisations, civil society, and private industry from around the world can engage with each other, review the latest research and policy innovations, and agree solutions for making the world safer and healthier. To that end, our mission is to help foster a genuinely multidisciplinary community of practice that is committed to working collaboratively to enhance global health security and eliminate disease, irrespective of its origin or source.”
SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology, and Biosecurity Conference in Africa
“Join us for the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa, a groundbreaking event that brings together experts, researchers, and enthusiasts in the field of synthetic biology. This in-person conference will take place at the Laico Regency Hotel from Wed, Jul 17, 2024 to Friday, Jul 19, 2024.”
“Get ready to dive into the exciting world of synthetic biology and explore its potential applications in Africa. From cutting-edge research to innovative solutions, this conference offers a unique opportunity to learn, network, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.”
“Discover the latest advancements, trends, and challenges in synthetic biology through engaging keynote speeches, interactive workshops, and thought-provoking panel discussions. Immerse yourself in a vibrant atmosphere where ideas flow freely and new connections are made.”
“Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in synthetic biology, this conference provides a platform to expand your knowledge, exchange ideas, and contribute to the growth of the field in Africa.”
“Don’t miss out on this extraordinary event that promises to shape the future of synthetic biology and biosecurity in Africa. Mark your calendars and join us at the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa!”
Learn more and register here.
Applied Biosafety Call for Papers, Special Issue: Biosafety and Biosecurity for Potential Pandemic Pathogens and Dual Use Research of Concern
“The fields of biosafety and biosecurity are crucial to managing risks associated with Potential Pandemic Pathogens (PPPs) and Dual Use Research of Concern (DURC), particularly as novel and reemerging pathogens increasingly impact global health. The Editors of Applied Biosafety are pleased to announce a forthcoming Special Issue focused on the myriad of risks associated with handling, transporting, and researching PPPs and DURC, as well as the measures needed to mitigate these risks effectively. This special issue aims to review and scrutinize existing and forthcoming government policies and regulations to identify gaps in addressing these concerns. It will also explore the integral role played by biosafety and biosecurity professionals in shaping policy and guidance.”
Learn more here.
Job Openings at the Institute for Progress
Senior Biotechnology Fellow
“Our biotechnology portfolio explores how we can advance policies that improve U.S. state capacity to accelerate and shape promising innovations in biotechnology and biotechnology governance. Innovations in biology may finally deliver cures to HIV, malaria, influenza, and some cancers. New AI models are unfolding the secrets of the molecular world before our eyes. Spurred by the urgency of the pandemic, we are now closer than ever before to developing technologies to prevent future such outbreaks.”
“Biotechnology fellows are expected to have a keen interest in these issues. Under the guidance of the IFP team, they will explore and become experts in specific biotechnology topics, both from a technology and policy perspective. Fellows will interact with policymakers, write articles and white-papers, and more. We encourage fellows to pursue creative routes that they think might have significant counterfactual policy impact.”
Biotechnology Fellow
“Biotechnology fellows are expected to have a keen interest in these issues and the ways the U.S. government supports and oversees them. Under the guidance of the IFP team, they will explore and become experts in specific biotechnology topics, both from a technical and policy perspective. Fellows will interact with policymakers, write articles and white papers, and more – we encourage fellows to pursue creative routes that they think might have significant counterfactual policy impact.”
Learn more and apply to these positions here.
Job Opening at Blueprint Biosecurity
“Blueprint Biosecurity is seeking a full-time Program Director to build and lead our portfolio of work on personal protective equipment (PPE). We are seeking a proactive leader who thrives in a dynamic and evolving environment. You will have a high degree of autonomy to design and steer a pioneering program that aims to advance the state of PPE for pandemic prevention. This effort will build on the roadmap for Pandemic Proof PPE, developing goals and objectives to translate our ambitious vision into tangible outcomes. A successful candidate will be excited about building an effort from the ground up and willing to pivot and iterate to find ways to succeed.”
“In this role, you will be working collaboratively with other teams within and external to Blueprint Biosecurity. The ideal candidate will have excellent interpersonal abilities and strong skills in project management, strategic prioritization, research, and analysis.”
Learn more and apply here.



