This edition of the Pandora Report covers the United States’ accusations against the Russian Federation regarding the use of chloropicrin and riot control agents “as a method of warfare” in Ukraine, the Biden administration’s new framework for nucleic acid synthesis screening, DHS’ new guidelines on preventing AI threats to critical infrastructure and CBRN weapons design, and more.
United States Accuses Russia of Violating Chemical Weapons Convention, Announces Further Sanctions
On Wednesday, the US officially accused Russia of violating the CWC by deploying chloropicrin weapons against Ukrainian forces and using riot control agents “as a method of warfare” in Ukraine. Chloropicrin (PS), a choking agent, was first used during World War I, and it is explicitly banned under the CWC, as is the use of RCAs not included in the CWC’s schedules when used as a method of warfare. In a statement, the US Department of State said “The use of such chemicals is not an isolated incident, and is probably driven by Russian forces’ desire to dislodge Ukrainian forces from fortified positions and achieve tactical gains on the battlefield. Russia’s ongoing disregard for its obligations to the CWC comes from the same playbook as its operations to poison Aleksey Navalny and Sergei and Yulia Skripal with Novichok nerve agents.”

The State Department and the Department of the Treasury have announced sanctions against more than 280 individuals and entities, including more than 80 known to be engaged in sanction evasion or that are related to Russia’s CBW and defense industrial base. In its statement, the Treasury said “Treasury is also targeting three Russia-based entities and two individuals involved in procuring items for military institutes involved in Russia’s chemical and biological weapons programs. In coordination, the Department of State is separately designating three Russian government entities associated with Russia’s chemical and biological weapons programs and four Russian companies contributing to such entities. These actions are being taken concurrent with the Department of State’s imposition of Chemical and Biological Weapons Control and Warfare Elimination Act of 1991 (the CBW Act) sanctions on Russia over its use of the chemical weapon chloropicrin against Ukrainian troops.”
White House Releases Framework for Nucleic Acid Synthesis Screening
On Monday, the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) announced the release of its Framework on Nucleic Acid Synthesis Screening, as directed by President Biden’s Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development of Artificial Intelligence. The framework aims to help manage AI risks so that its benefits can be used in synthetic biology by encouraging “providers of synthetic nucleic acids to implement comprehensive, scalable, and verifiable screening mechanisms.”
In its statement, OSTP said “Through the AI executive order, President Biden has directed action on AI across the economy, including AI applied to biotechnology and synthetic biology. Nucleic acids serve as the critical building blocks for life science research and development (R&D) —including the development of new biomedical products, novel strategies for recycling and energy production, and the creation of new classes of materials. It is essential that nucleic acid synthesis technologies are appropriately managed to promote positive outcomes and prevent nefarious uses. Nucleic acid synthesis screening is an effective, targeted measure to mitigate the potential for misuse of AI-enabled biotechnologies.”
“This framework recommends that providers of synthetic nucleic acids screen purchases to prevent misuse, building on recent guidance from the Department of Health and Human Services. The National Institute of Standards and Technology will further support implementation of this framework by engaging with industry to develop technical standards for screening, as directed by the Executive Order.”
“As directed by the Executive Order, within 180 days of the release of this framework, federal research funding agencies will require recipients of federal R&D funds to procure synthetic nucleic acids only from providers that implement these best practices. While this framework establishes requirements for federally funded research, it is anticipated that these requirements may be adopted more broadly by other research funders.”
DHS Warns AI Could Be Used to Design WMD
This week, the Department of Homeland Security released a new report discussing potential ways that artificial intelligence could be used to help design chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapons as well as guidelines addressing this threat. DHS also released guidelines on securing critical infrastructure in light of advancements in AI, as required by President Biden’s Executive Order (EO) 14110, “Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)”.
The report on CBRN weapons and AI risks, which was submitted to President Biden, “…identifies trends within the growing AI field along with distinct types of AI and machine learning models that might enable or exacerbate biological or chemical threats to the U.S. It also includes national security threat mitigation techniques through oversight of the training, deployment, publication and use of AI models and the data used to create them — particularly regarding how safety evaluations and guardrails can be leveraged in these instances.”
Meanwhile, the guidance on protecting critical infrastructure focuses its attention on water treatment facilities and supplies, telecom operations, and power grids in light of recent cyber attacks targeting these kinds of facilities. “AI can present transformative solutions for U.S. critical infrastructure, and it also carries the risk of making those systems vulnerable in new ways to critical failures, physical attacks, and cyber attacks. Our Department is taking steps to identify and mitigate those threats,” said Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro Mayorkas in a press release.
Asia Centre for Health Security Opens in Singapore
Recently, the Asia Centre for Health Security (ACHS) opened its doors at the National University of Singapore’s Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health, marking an important development for health security research in the region. In a statement about ACHS, the Centre’s Director and Vice Dean of Saw Swee Hock SPH, Hsu Li Yang, told The Straits Times “The focus includes all manner of catastrophic biological threats, rather than just zoonoses. So laboratory biosafety and deliberately released or man-made biological agents are also a part of our work…Rather than hardcore biomedical science and technology, we work on health systems, global health law and regulations, and global relations where it pertains to health security issues.”
Joyce Teo explains in the same piece that “Established with the help of generous philanthropic funding, ACHS is steered by a multidisciplinary team with expertise in areas from public health and clinical practice to global health law and policymaking. It will work closely with the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies at Nanyang Technological University in areas such as research and training.”

“National Intelligence Estimate: Dynamics Shaping Global Health Security In the Next Decade”
The Office of the Director of National Intelligence recently approved for release this December 2023 National Intelligence Estimate (NIE) from the National Intelligence Council. The estimate’s key takeaway is that “During the next decade, the global health security landscape will be stressed by climate and societal changes, strained health infrastructure and capacity, and eroding global health governance. Regardless of the severity and scope, global health emergencies are likely to continue to strain national health systems, particularly disadvantaging poorer countries, as well as encourage and result in responses that are constrained by major power competition. Nonetheless, promising health initiatives utilized during the COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with burgeoning technological advances, are likely to help fill some shortfalls, but will require overcoming competitive approaches and geopolitical rivalry.”
“Public Health Preparedness: HHS Should Address Strategic National Stockpile Coordination Challenges”
From the Government Accountability Office: “The federal government coordinates with states, localities, territories, and Tribes to distribute life-saving medicines and supplies from the Strategic National Stockpile during public health emergencies…But during recent public health responses, such as COVID-19 and mpox, jurisdictions weren’t clear on how and from whom to request supplies, causing confusion and delays. Additionally, some Tribal officials cited challenges with having the facilities needed to receive and store delivered supplies…Our recommendations address this and other issues we found.”
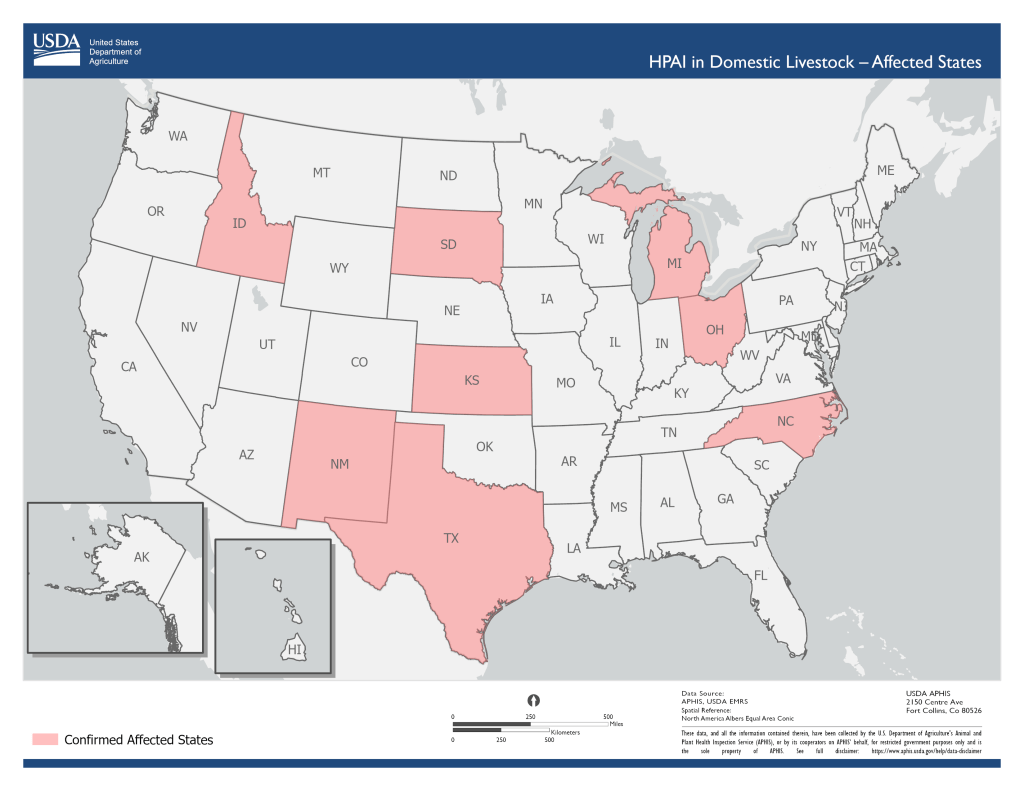
“Who Could Catch Bird Flu First? These Experts Have an Idea, and a Way to Help.”
Erin M. Sorrell, Monica Schoch-Spana and Meghan F. Davis recently published this opinion piece in The New York Times discussing the need to improve protections for those working in the farming industry. They write in part “So far, bird flu testing of this cohort has been woefully inadequate. Testing is usually under the purview of state authorities following federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines. Tests are recommended for symptomatic workers. The exact number of dairy workers and other people who have so far been tested for H5N1 is not publicly available at the federal level. There is no excuse to continue only limited testing of this vulnerable population. Any serious surveillance efforts of H5N1 demand that the country do better to ensure proper testing and health care is provided to these workers now, lest we risk being caught flat-footed by a new pandemic so soon after Covid.”
“WHO Overturns Dogma on Airborne Disease Spread. The CDC Might Not Act on It.”
Amy Maxmen discusses the CDC’s potential response to recent changes in how the WHO defines airborne disease spread in this piece for KFF Health News: “However, the WHO report stops short of prescribing actions that governments, hospitals, and the public should take in response. It remains to be seen how the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will act on this information in its own guidance for infection control in health care settings.”
“A Pandemic Agreement Is Within Reach”
Anita Cicero and Alexandra Phelan recently authored this editorial piece for Science, explaining their introduction “At the end of May, 194 member states of the World Health Organization (WHO) will meet for the World Health Assembly. Negotiations underway now will determine whether they vote then to adopt a pandemic agreement. For the past 2 years, discussions have focused on articulating essential components of a robust and equitable architecture for pandemic preparedness and response. Despite this, talks have failed to produce sufficient consensus on a detailed draft, prompting the intergovernmental negotiating body to propose a “streamlined” version. The new text, released on 16 April, consolidates provisions for research and development, technology transfer, pathogen access and benefit sharing (including pandemic products such as medicines and vaccines), with many particulars deferred to future procedures. Ultimately, success of the agreement will depend on these details and implementation. Nevertheless, member states shouldn’t bypass the consensus reached to date, but continue progress to adopt this agreement.”
CARB-X 2023 Annual Report
Boston University’s Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) recently released its 2023 Annual Report, which identifies several trends, including:
- “Rapid diagnostics expanded during the COVID-19 pandemic, leaving product developers poised to capitalize on their investments by embracing new sample types and pathogens;
- More than half of therapeutics applicants were in the hit-to-lead stage, reinforcing the evident dearth of oral therapeutics in the clinical and preclinical pipelines; and
- CARB-X received expressions of interest from the vaccine community in response to the lack of vaccines in development for K. pneumoniae, ExPEC, S. aureus, A baumannii, and N. gonorrhoeae.“
“Ralph Baric, Whose Virology Techniques Were Used in Wuhan, Testified That Lab Leak Was Possible”
Katherine Eban, co-author of the widely criticized Vanity Fair and ProPublica article discussing the possibility of a lab leak origin of the COVID-19 pandemic at the Wuhan Insitute of Virology, recently published this Vanity Fair piece, writing “The UNC coronavirologist who has collaborated on gain-of-function research with the Wuhan Institute of Virology’s Shi Zhengli, told congressional investigators that he has long worried about biosafety protocols inside China. Though he thinks it’s far more likely COVID-19 originated in nature, he said of a possible laboratory escape, “You can’t rule that out.”’
“A Virus Hunter’s Struggle for Respect in Post-COVID China”
In this piece for Think Global Health, Yanzhong Huang discusses how Zhang Yongzhen, the scientist who first published the genome sequence of SARS-CoV-2, has struggled with his employer-the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center-as China moves on from COVID-19: “In a shocking turn of events, Zhang Yongzhen, PhD, the internationally renowned scientist credited with first publishing the genome sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, staged a sit-in protest outside his laboratory at the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (SPHCC). In a country that values stability and obedience, this dramatic action quickly captured the attention of both Chinese and international media. As Edward Holmes, a leading virologist at the University of Sydney, remarked in Nature, “it is unfathomable to me to have a scientist of that caliber sleeping outside his lab.”‘
“China Has a Controversial Plan for Brain-Computer Interfaces”
Emily Mullin discusses Chinese aspirations of cognitive enhancement in this Wired piece, explaining in part ‘“China is not the least bit shy about this,” he says, referring to ethical guidelines released by the Communist Party in February 2024 that include cognitive enhancement of healthy people as a goal of Chinese BCI research. A translation of the guidelines by CSET says, “Nonmedical purposes such as attention modulation, sleep regulation, memory regulation, and exoskeletons for augmentative BCI technologies should be explored and developed to a certain extent, provided there is strict regulation and clear benefit.”’
“The translated Chinese guidelines go on to say that BCI technology should avoid replacing or weakening human decisionmaking capabilities “before it is proven to surpass human levels and gains societal consensus, and avoid research that significantly interferes with or blurs human autonomy and self-awareness.”’
“The Czech Illegals: Husband and Wife Outed as GRU Spies Aiding Bombings and Poisonings Across Europe”
Michael Weiss, Roman Dobrokhotov, and Christo Grozev recently published this investigative piece in The Insider covering the work of Elena and Nikolai Šapošnikov’s support of GRU Unit 29155, explaining in part “While both Šapošnikov spouses engaged in espionage for Russia assisted GRU’s sabotage operations, the wife, Šapošnikova, 62, appears to have been directly integrated with Unit 29155, as evidenced both by findings by the Czech investigators and by The Insider’s independent discovery of documentary evidence. As such, Czech investigators have concluded, she likely directed and supervised her husband’s – and possibly their son’s – activities in support of Russian state interests. The family’s clandestine duties ranged from intelligence-gathering to logistical facilitation, providing safe havens, recruitment efforts, and even aiding in securing physical access for GRU operatives conducting sabotage missions.”
“UNSCR 1540 at 20 Years”
Christina McAllister and Annie Trentham recently published this commentary piece with the Stimson Center covering the first two decades since UNSCR 1540 was passed. They explain in their introduction, “United Nations (UN) Security Council Resolution 1540 marked a round birthday of 20 years on April 28, approaching its age of majority in a very different world to the one into which it was born two decades ago. Obligating all UN member states to implement measures preventing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), delivery systems, and related materials, particularly to non-state actors, its passage in 2004 was a historic achievement by an international community shaken by the 2001 terror attacks on the United States as well as the exposure of A.Q. Khan’s nuclear proliferation activities. It is hard to imagine such unified action today, amid the geopolitical tensions that consume so much valuable multilateral energy and resources. Yet while the international context has changed significantly since 2004, the need for Resolution 1540 has only grown, even while implementation challenges remain.”
First Issue of the UNSCR 1540 Compass
The UN Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute (UNICRI) recently released the first edition of the UNSCR 1540 Compass. In a statement about the new publication, UNICRI Acting Director Leif Villadsen said “This new e-journal comprises one of the ways in which the Institute is committed to advancing the objectives of UNSCR 1540 and bolstering the global non-proliferation framework. The publication aims to shed light on the impact, challenges and INTRO 9 opportunities of UNSCR 1540, as well as the work of the 1540 Committee. It also seeks to establish a dynamic platform for international dialogue and knowledge exchange among Member States, experts, practitioners, and organizations involved in implementing UNSCR 1540. Moreover, it will enable us to stay abreast of emerging trends, threats and risks. I trust that it will generate informed discussions and actionable insights that can help us forge better collective understanding of the field of non-proliferation as it stands today.”
Read the first issue here.
NEW-H5N1 What Do We Know So Far?
From Boston University Center on Emerging Infectious Diseases: “Cases of the H5N1 strain of avian flu have been reported in US dairy cattle since March 2024. As we have seen avian influenza (or “bird flu”) has the ability to be transmitted from birds to mammals such as cows and humans. We know that this strain of avian flu is transmittable to humans; in April 2024 a case was reported in a dairy farm worker who had been in contact with infected cattle.”
“This begs the question, how concerned should we be about future spread of H5N1 from animals to humans? And how does the risk of infection vary for farmers compared to the general population? Based on experience with other strains of avian flu, how do experts foresee this strain potentially evolving?”
“Join Boston University’s Center on Emerging Infectious Diseases for a discussion with experts in epidemiology, infectious diseases, and veterinary medicine as we unpack these questions and more.”
This virtual event will take place on May 9 at 10 am EST. Learn more and register here.
NEW-Biosafety and the Origin of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Evidence and Policy Implications
From Brookings: “The world just lived through the COVID-19 pandemic, with more than 7 million reported direct deaths globally, more than 775 million reported cases, more than 14 million indirect excess deaths, and likely millions more unreported deaths. Despite the devastating effects on people and economies around the world, we still do not know with certainty how the pandemic originated, with the two most likely hypotheses either a natural spillover from an animal host or a research lab leak. Finding an answer to this question is not just a matter of doing justice to the millions of victims of COVID-19—it will have significant ramifications for policy implementation to help prevent the next pandemic.”
“Importantly, the catastrophic impact of the COVID-19 disease has shown us that preventing the next pandemic and biosafety in general should be top of mind for researchers, regulators, policymakers and public health officials, and it will likely require an array of measures by private, public, and nongovernmental organizations. This includes reconsidering our early warning systems for emergent diseases from the natural world, and taking a closer look at research with dangerous pathogens in biolabs. Identifying the origins of the recent pandemic can help target those efforts.”
“On May 14, the Brookings Center on Regulation and Markets will address these complex questions. First, Alina Chan, scientific advisor at the Broad Institute, and Alison Young, Curtis B. Hurley chair in public affairs reporting at the University of Missouri School of Journalism, will explain why the origin of the SARS-CoV-2 virus matters for public policy. Then, a balanced expert panel will debate the two most likely origins: natural spillover or a leak from a lab. A final panel of biosafety experts will discuss what measures would be best suited to improve biosafety and reduce the risks for research-related lab incidents as well as future pandemics. This event is a part of the CRM series on Reimagining Modern-day Markets and Regulations.”
This online event will take place on May 14 at 1:30 pm EDT. Learn more and access the event here.
3rd International Biosecurity Virtual Symposium
From ABSA: “The Symposium will bring together biosecurity professionals from a wide range of disciplines with varying expertise to share their experiences and knowledge on diverse biosecurity topics. The Symposium will offer attendees an opportunity to learn the latest in biosecurity and have thought-provoking conversations about real-world biosecurity issues, concerns, and scenarios.”
This symposium will take place May 7-8. Learn more and register here.
Addressing the Challenges Posed by Chemical and Biological Weapons: Intensive Online Introductory Course for Students of Technical Disciplines
“SIPRI and the European Union Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Consortium (EUNPDC) invite graduate and postgraduate students of the technical or natural science disciplines to apply for an intensive online introductory course on chemical and biological weapons—their proliferation, the efforts to eliminate them, the various mechanisms used to control their spread—and endeavours underway to reduce the risk of chemical or biological agents in terrorist attacks. The course will take place online, during four half-days on 28–31 May 2024, 14:00 to 18:00 Central European Summer Time (CEST).”
“The course will cover the fundamentals of chemical and biological weapons as well as of missiles and other means of delivery; the history of chemical and biological warfare; the evolution of international norms against these weapons; the threats associated with potential terrorist uses of chemical and biological material; bioweapons and other related scientific advances; the current challenges posed by chemical weapons; arms control treaties; and mechanisms to curb the spread of dangerous substances, including export controls.”
“The course will also discuss the role of the EU institutions and industry to address the challenges mentioned above. The course will be instructed by renowned experts on non-proliferation, arms control, disarmament, export controls, verification and related subjects from SIPRI, other European research centres, think tanks and international organizations.”
Learn more and apply here.
Registration for GHS 2024 Now Open
Registration is now open for the Global Health Security 2024 conference in Sydney, Australia. This iteration will take place 18-21 June, 2024. The call for abstracts is also still open. “The mission of the Global Health Security conference is to provide a forum where leaders, researchers, policy-makers, and representatives from government, international organisations, civil society, and private industry from around the world can engage with each other, review the latest research and policy innovations, and agree solutions for making the world safer and healthier. To that end, our mission is to help foster a genuinely multidisciplinary community of practice that is committed to working collaboratively to enhance global health security and eliminate disease, irrespective of its origin or source.”
SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology, and Biosecurity Conference in Africa
“Join us for the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa, a groundbreaking event that brings together experts, researchers, and enthusiasts in the field of synthetic biology. This in-person conference will take place at the Laico Regency Hotel from Wed, Jul 17, 2024 to Friday, Jul 19, 2024.”
“Get ready to dive into the exciting world of synthetic biology and explore its potential applications in Africa. From cutting-edge research to innovative solutions, this conference offers a unique opportunity to learn, network, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.”
“Discover the latest advancements, trends, and challenges in synthetic biology through engaging keynote speeches, interactive workshops, and thought-provoking panel discussions. Immerse yourself in a vibrant atmosphere where ideas flow freely and new connections are made.”
“Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in synthetic biology, this conference provides a platform to expand your knowledge, exchange ideas, and contribute to the growth of the field in Africa.”
“Don’t miss out on this extraordinary event that promises to shape the future of synthetic biology and biosecurity in Africa. Mark your calendars and join us at the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa!”
Learn more and register here.