Happy Friday! This week’s edition of the Pandora Report covers HHS’ launch of a probe into the cyber attack on Change Healthcare, the IC’s annual threat assessment, new publications and professional opportunities, and more.
Biodefense PhD Student Lands Fellowship With National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology
“Aishwarya Sriraman, Biodefense PhD student, is starting a fellowship with the National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology, a legislative branch advisory entity charged with conducting a review of how emerging biotechnologies will shape current and future activities of the Department of Defense. The fellowship will provide an exciting opportunity to gain firsthand policy and research experience working at the intersection of national security and emerging biotechnology. She will specifically be working with the Policy and Research team focused on partnerships and bioliteracy.”
HHS Opens Probe Into UnitedHealth Cyber Attack
The US Department of Health and Human Services announced Wednesday that it has opened an investigation into the February 21 cyber attack targeting a subsidiary of United Health-Change Healthcare. The aim of the investigation is to determine if there was any breach of protected health data and to see if UnitedHealth Group abided by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. ‘”Given the unprecedented magnitude of this cyberattack and in the best interest of patients and health care providers” the HHS Office for Civil Rights is initiating an investigation into the incident, the health department said.”
Secretary of HHS Xavier Becerra and Acting Secretary of the Department of Labor Julie A. Su said in a letter regarding the issue “In a situation such as this, the government and private sector must work together to help providers make payroll and deliver timely care to the American people. The Biden-Harris Administration has taken action by removing challenges for health care providers and addressing this cyberattack head on. Now, we are asking private sector leaders across the health care industry – especially other payers – to meet the moment.”
“The Biden-Harris Administration remains committed to ensuring that all Americans can access needed care in spite of this cyberattack. We urge the private sector to quickly identify and carry out solutions. Specifically, we call on UHG, other insurance companies, clearinghouses, and health care entities to take additional actions to mitigate the harms this attack places on patients and providers, particularly our safety net providers.”
Reuters explained in its reporting that Change Healthcare “processes about 50% of medical claims in the U.S. for around 900,000 physicians, 33,000 pharmacies, 5,500 hospitals and 600 laboratories.”
UnitedHealth has indicated it will cooperate with the investigation. It has yet to comment on what patient data may have been exposed by the attack.
Annual IC Threat Assessment Includes Warnings About Biotechnology, CBW
The Intelligence Community’s recently-released annual threat assessment included several sections dedicated to threats and challenges posed by advancing biotechnology and WMD proliferation. On biological weapons, the assessment explains “Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea probably maintain the capability to produce and use pathogens and toxins, and China and Russia have proven adept at manipulating the information space to reduce trust and confidence in countermeasures and U.S. biotechnology and research.”
It also outlines the potential for CW use to grow, explaining “The use of chemical weapons, particularly in situations other than state-on-state military operations, could increase in the near future. During the past decade, state and non-state actors have used chemical warfare agents in a range of scenarios, including the Syrian military’s use of chlorine and sarin against opposition groups and civilians, and North Korea’s and Russia’s use of chemical agents in targeted killings. More state actors could use chemicals in operations against dissidents, defectors, and other perceived enemies of the state; protestors under the guise of quelling domestic unrest; or against their own civilian or refugee populations.”
Finally, it identifies biotechnology and related biosecurity issues as key challenges (alongside AI) requiring cooperative global solutions. However, it notes such cooperation is harmed by authoritarian governments like those in China and Russia: “This competition also exploits technological advancements— such as AI, biotechnologies and related biosecurity, the development and production of microelectronics, and potential quantum developments—to gain stronger sway over worldwide narratives affecting the global geopolitical balance, including influence within it. The fields of AI and biotechnology, in particular, are rapidly advancing, and convergences among various fields of science and technology probably will result in further significant breakthroughs. The accelerating effects of climate change are placing more of the world’s population, particularly in low- and middleincome countries, at greater risk from extreme weather, food and water insecurity, and humanitarian disasters, fueling migration flows and increasing the risks of future pandemics as pathogens exploit the changing environment.”
More Than 90 Prominent Biologists, Other Scientists Sign Agreement Aiming to Mitigate AI Bioweapon Risk
The New York Times recently reported that “…over 90 biologists and other scientists who specialize in A.I. technologies used to design new proteins — the microscopic mechanisms that drive all creations in biology — have signed an agreement that seeks to ensure that their A.I.-aided research will move forward without exposing the world to serious harm.”
In their agreement, they explain “Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are creating unprecedented opportunities for life science research, including by enabling the design of functional biological molecules, especially proteins. This application of AI for protein design holds immense potential to enhance our understanding of the world and help address some of humanity’s most pressing challenges by enabling rapid responses to infectious disease outbreaks, curing numerous diseases, unlocking sustainable sources of energy, helping to mitigate climate change, and more.”
“As scientists engaged in this work, we believe the benefits of current AI technologies for protein design far outweigh the potential for harm and we would like to ensure our research remains beneficial for all going forward. Given anticipated advances in this field, a new proactive risk management approach may be required to mitigate the potential of developing AI technologies that could be misused, intentionally or otherwise, to cause harm. We are therefore motivated as a community to articulate a set of values and principles to guide the responsible development of AI technologies in the field of protein design. These values include safety, security, equity, international collaboration, openness, responsibility, and pursuing research for the benefit of society. Furthermore, we as signatories voluntarily agree to a set of specific, actionable commitments informed by these values and principles and outlined here. We will work together with global stakeholders across academia, governments, civil society, and the private sector to ensure that this technology develops in a responsible and trustworthy manner and that it is safe, secure, and beneficial for all.”‘
Read more here.

“Hidden in Plain Sight: the Next Biosecurity Threat”
This commentary piece was co-authored by Biodefense PhD Program alumnus Daniel M Gerstein. In it, Gerstein and his co-authors tackle key challenges in enforcing the International Health Regulations, comparing global responses to China’s delayed notification of the emergence of COVID-19 to the WHO with South Africa’s prompt notification of the emergence of the Omicron variant. They write in part, “The message is now clear: Keep quiet as long as possible to keep your hotels and beaches full, trade going and air travel open. There will be no penalty if you delay reporting. There will be no penalty if you refuse or delay access to the WHO or other specialists….In Geneva, Switzerland, negotiations on a global pandemic preparedness treaty stalled where they were predicted to stall: who gives what to whom and for how much?”
“If an international agreement does progress, to be effective it must “have teeth, but they rarely do,” commented the executive director of the American Public Health Association. If Geneva produced any agreement, the United States could be a party only with Senate ratification. The likelihood of that level of bipartisan cooperation is (charitably) remote.”‘
“Learnings from COVID-19 for Future Respiratory Pathogen Pandemic Preparedness: A Summary of the Literature”
From WHO: “A scoping literature review of learnings from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic was commissioned by WHO to inform operational priorities for future respiratory pathogen pandemic preparedness. The learnings are grouped according to WHO’s subsystems for health emergency preparedness, response and resilience. Key takeaway messages include: 1) Preparedness works; 2) Health is everyone’s business; 3) No one is safe until everyone is safe; and 4) Response must be agile and adaptive. The review will support pandemic planners at all levels to develop and update preparedness and response plans.
“The COVID-19 Pandemic at Year Four: The Imperative for Global Health Solidarity”
Syra Madad recently authored this blog post for the New York Academy of Sciences, writing in part “This month marks a solemn milestone: the four-year anniversary of the COVID-19 pandemic declaration by the World Health Organization. During this period, the virus has caused the deaths of over seven million individuals globally—a figure that is vastly undercounted, with actual losses likely two to three times higher. This number also includes over one million COVID-19 deaths in the United States alone. A recent analysis of excess mortality in the U.S., which provides an estimation of deaths that likely would not have occurred under normal, non-pandemic conditions, has found that in the first two years of the pandemic many of the excess deaths that were attributed to natural causes were actually uncounted COVID-19 deaths. This points to a significant underestimation of the pandemic’s true death toll, let alone the impact on livelihoods and disability caused by this virus.”
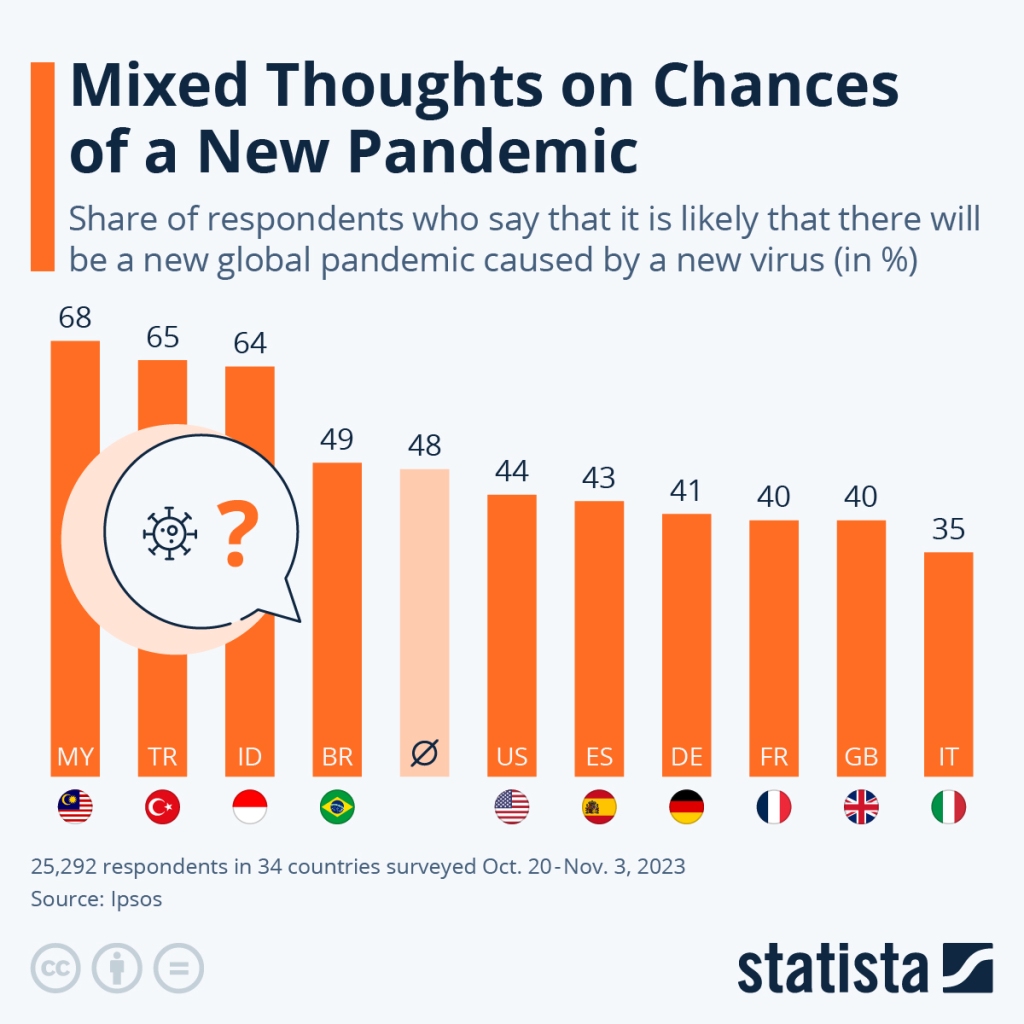
“Mixed Thoughts on Chances of a New Pandemic”
Statista’s Anna Fleck recently authored this piece rocused on public perceptions of the chances of a new pandemic emerging. It covers the results of a survey, with the results displayed in this chart:
“Banning Gain-of-Function Research Would Do Far More Harm Than Good”
Judy Minkoff tackles the debate over a recently-passed House bill that aims to halt federal funding for all research involving gain of function work in this piece for MedPage Today. She writes in her introduction “The Republican-controlled House of Representatives recently approved an amendmentopens in a new tab or window to the 2024 House spending billopens in a new tab or window that prohibits federal funding for all gain-of-function (GoF) research — that which endows a pathogen with a new or enhanced property. Many scientists are hopeful that the bill will fail in the Democratic-controlled Senate, but if this vaguely-worded provision becomes law, it could halt research pertaining to a wide variety of public concerns, including gene therapy, cancer treatment, and pandemic preparedness.”
“Congressional attacks on science extend beyond this amendment. House Republicans, holding a majority in the Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemicopens in a new tab or window, have skewed the narrative on COVID-19 toward an unsupported link with GoF research, citing communications between government officials and the authors of a controversial scientific publicationopens in a new tab or window as proof of a conspiracyopens in a new tab or window to suppress the lab origin theory. Rather than leveraging their authority to foster balanced discussion among experts in an effort to learn from the pandemic, the subcommittee has engaged in months of hearings on this single topic.”
“The Joint Assessment Mechanism: Discerning the Source of High-Consequence Biological Events of Unknown Origin”
A new white paper from NTI: “The white paper, which reflects several rounds of consultations with an international group of technical and policy experts, diplomats, and other key stakeholders in the field of pandemic preparedness, provides an in-depth argument for establishing the JAM to fill the critical gap among existing UN mechanisms and entities. The paper suggests that the JAM should be based within the Office of the UN Secretary General—serving as an interface between the World Health Organization (WHO), the UN Secretary-General’s Mechanism, and other key stakeholders—where it can provide an ongoing baseline assessment of current biological risks.”
“Bioliteracy for the Age of Biology”
From the National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology: ‘“Bioliteracy” is the concept of imbuing people, personnel, or teams with an understanding of — and ability to engage with — biology and biotechnology. The Commission believes that all Americans—including policymakers in the U.S. Government, students at all levels of education, current and future biotechnology workers, and the broader public—should one day be as comfortable using and engaging with biotechnology in the same way that they do with computers and software in their daily lives and within society.”
“Increased bioliteracy across all segments of the population will help Americans realize the potential of a robust U.S. biotechnology ecosystem that maximizes the promises of biotechnology for the benefit of all citizens.”
Read more here.
“The Viral Most Wanted-The Filoviruses”
CEPI’s latest installment of the Viral Most Wanted tackles the filoviruses. Its exciting introduction explains: “Dr Jean-Jacques Muyembe was a newly-qualified microbiologist working as a field epidemiologist when he got a call in 1976 to help investigate an outbreak. A pernicious disease had taken hold in the village of Yambuku in central Zaire, now the Democratic Republic of Congo. People were dying in large numbers of the infection – one that appeared at first to be like malaria or typhoid or yellow fever, but was clearly something even worse.”
“Muyembe knew that some of the Belgian nuns working in the village had been vaccinated against yellow fever and typhoid, yet this infection was easily flooring those defences. It was a swift and gruesome new killer.”
“Reflecting on his experience with these first few patients, Muyembe said the most striking thing was when he drew blood from them. Removing the syringe and needle, he found that the tiny puncture hole would continue to gush blood. It was the first time he’d seen such a thing, he recalled, and he knew it was an ominous sign.”
“After asking one of the infected nuns to fly back with him to Kinshasa, Muyembe took blood samples from her and sent them to Belgium for testing. The analysis that followed produced a shocking result. The blood of the nun, who by now had been killed by the disease, was infected with a virus that caused an acute haemorrhagic fever – one that scientists now describe as “one of the most lethal infections you can think of”.”
“The pathogen swiftly became known as Ebolavirus after the river that runs near Yambuku where it infected the villagers and the nuns. It was also swiftly recognised as a member of the Filovirus family – one of The Viral Most Wanted.“
“Response is Failure in the Primary Mission of Preventing CBW”
JP Zanders recently published this piece on The Trench: “The Global Partnership against the Spread of Materials and Weapons of Mass Destruction has now been around for over two decades. In the wake of the terrorist attacks against the US in September 2001, it started out as an effort to mobilise the resources of the G8 members to prevent terrorist acquisition of nuclear, biological and chemical weapons, and related materials. The weapons, technologies and skills available from the former Soviet Union presented a significant proliferation risk, which the US was already addressing through the Cooperative Threat Reduction (CTR) programme.”
“Now comprising 31 members, the Global Partnership (GP) played a key role in assisting Russia with the destruction of its chemical weapons (CW) and dismantling the biological weapons (BW) infrastructure in other former Soviet states. Since then, it has expanded its mission of preventing the re-emergence of BW and CW to different parts of the world and tackles multiple types of proliferation threats. Among the latest is Russia’s massive disinformation campaign against the collective threat reduction activities in former Soviet republics to justify the invasion of Ukraine and interference in other countries.”
“To discuss the GP’s past and present work and the response to the latest challenges, I interviewed Trevor Smith, Senior Program Manager of the Biological and Chemical Security Weapons Threat Reduction Program run by Global Affairs Canada. The interview took place on 31 January 2024.”
“Flashback: When Nerve Gas Testing Killed 7,000 Sheep Near Dugway in Utah”
This Axios SLC Old News piece discusses the deaths of more than 7,000 sheep thirty miles away from the US Army’s Dugway Proving Grounds in 1968. “The Army confirmed in a 1978 report — which wasn’t publicly released until the Salt Lake Tribune obtained it 20 years later — that “incontrovertible” evidence showed VX was to blame.”
In 2018, Al Mauroni published this article with the Modern War Institute discussing this incident and its implications, writing in part “Politics and perception had essentially overwhelmed science and reason. This probably wasn’t the first time that this had happened, nor would it be the last. The point of this narrative, other than as a historical observation, is to reflect on what this has done to the preparedness of US military forces today. Yes, the United States no longer has a chemical weapons program. Yes, there is a Chemical Weapons Convention that nearly all nations of the world have signed, effectively eliminating chemical weapons as a future tool of warfare—we hope. North Korea is a particular exception to that treaty, and most assumptions are that, if North Korea goes to war against South Korea, it will use thousands of tons of chemical warfare agents against US forces. Are we confident that our forces have the necessary gear to protect themselves and sustain combat operations in such an environment? And do we have plans for how US military bases and ports will recover after being attacked with chemical weapons?”
“COLUMN: Which Terrorist Organization Suffers More Casualties in Its Attacks? Al Qaeda, ISIS, Hamas, or Iran-backed Militia Groups?”
Schar School associate professor Mahmut Cengiz recently published this commentary piece with Homeland Security Today, explaining in his introduction “Despite being a top priority on government agendas for the past few decades, it appears that no counterterrorism policies have been successful in combatting terrorist groups. Thousands of terrorist attacks and fatalities are still being recorded each year by terrorism databases. For instance, in 2023, the Global Terrorism and Trends Analysis Center (GTTAC) Records of Incidents Database (GRID) documented 7,480 terrorist attacks that led to the death of 23,119 individuals.”
What We’re Listening To 🎧
Poisons and Pestilence, 24 Movie Special: Outbreak and Contagion with Saskia Popescu
“In our first ever movie review special, Dr Saskia Popescu reviews the classics Contagion (2011) and Outbreak (1995)…”
NEW: Addressing the Challenges Posed by Chemical and Biological Weapons: Intensive Online Introductory Course for Students of Technical Disciplines
“SIPRI and the European Union Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Consortium (EUNPDC) invite graduate and postgraduate students of the technical or natural science disciplines to apply for an intensive online introductory course on chemical and biological weapons—their proliferation, the efforts to eliminate them, the various mechanisms used to control their spread—and endeavours underway to reduce the risk of chemical or biological agents in terrorist attacks. The course will take place online, during four half-days on 28–31 May 2024, 14:00 to 18:00 Central European Summer Time (CEST).”
“The course will cover the fundamentals of chemical and biological weapons as well as of missiles and other means of delivery; the history of chemical and biological warfare; the evolution of international norms against these weapons; the threats associated with potential terrorist uses of chemical and biological material; bioweapons and other related scientific advances; the current challenges posed by chemical weapons; arms control treaties; and mechanisms to curb the spread of dangerous substances, including export controls.”
“The course will also discuss the role of the EU institutions and industry to address the challenges mentioned above. The course will be instructed by renowned experts on non-proliferation, arms control, disarmament, export controls, verification and related subjects from SIPRI, other European research centres, think tanks and international organizations.”
Learn more and apply here.
Artificial Intelligence and Automated Laboratories for Biotechnology: Leveraging Opportunities and Mitigating Risks
From the National Academies’ Board on Life Sciences: “Please join us April 3-4, 2024 for a hybrid workshop on the opportunities and mitigation of risks of the use of artificial intelligence and automated laboratories (i.e., self-driving labs) for biotechnology.”
“The workshop will consider opportunities to leverage AI and laboratory automation capabilities for discovery and development, explore methods and approaches to identify, track, and forecast the domestic and international development of such technologies, and convene experts across sectors to highlight recent advances and explore implications for the development and use of these technologies.”
Learn more and register here.
Launch of the 2024 National Blueprint on Biodefense
From the Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense: “On the 10th anniversary of its inception, the Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense will release its 2024 National Blueprint on Biodefense: Immediate Action Needed to Defend Against Biological Threats.”
“Please join us for this momentous event at the Congressional Auditorium, Capitol Visitor Center, on April 17th at 4:30pm.”
“The Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense (formerly the Blue Ribbon Study Panel on Biodefense) was established in 2014 to provide a comprehensive assessment of the state of United States biodefense efforts and to issue recommendations that foster change. Subsequently, the Commission has briefed White House Administrations (including then Vice President Biden); testified before Congress; convened numerous meetings with experts; released 12 reports; produced the graphic novel Germ Warfare; and mobilized biodefense conversations and actions in the private and public sectors.”
Learn more and register here.
Registration for GHS 2024 Now Open
Registration is now open for the Global Health Security 2024 conference in Sydney, Australia. This iteration will take place 18-21 June, 2024. The call for abstracts is also still open. “The mission of the Global Health Security conference is to provide a forum where leaders, researchers, policy-makers, and representatives from government, international organisations, civil society, and private industry from around the world can engage with each other, review the latest research and policy innovations, and agree solutions for making the world safer and healthier. To that end, our mission is to help foster a genuinely multidisciplinary community of practice that is committed to working collaboratively to enhance global health security and eliminate disease, irrespective of its origin or source.”
SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology, and Biosecurity Conference in Africa
“Join us for the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa, a groundbreaking event that brings together experts, researchers, and enthusiasts in the field of synthetic biology. This in-person conference will take place at the Laico Regency Hotel from Wed, Jul 17, 2024 to Friday, Jul 19, 2024.”
“Get ready to dive into the exciting world of synthetic biology and explore its potential applications in Africa. From cutting-edge research to innovative solutions, this conference offers a unique opportunity to learn, network, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.”
“Discover the latest advancements, trends, and challenges in synthetic biology through engaging keynote speeches, interactive workshops, and thought-provoking panel discussions. Immerse yourself in a vibrant atmosphere where ideas flow freely and new connections are made.”
“Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in synthetic biology, this conference provides a platform to expand your knowledge, exchange ideas, and contribute to the growth of the field in Africa.”
“Don’t miss out on this extraordinary event that promises to shape the future of synthetic biology and biosecurity in Africa. Mark your calendars and join us at the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa!”
Learn more and register here.
Eighth Annual Next Generation for Biosecurity Competition Open for Applications
“The Eighth Annual Next Generation for Biosecurity Competition is now open. NTI | bio hosts this competition to provide a platform for the next generation of global leaders in biosecurity to develop original concepts and share them with the wider biosecurity community. This year’s co-sponsors include 80,000 Hours, the Global Health Security Network, the iGEM Foundation, the International Federation of Biosafety Associations, the Next Generation Global Health Security Network, Pandemic Action Network, SynBio Africa, and Women of Color Advancing Peace, Security, and Conflict Transformation.“
“This year, the competition invites innovative and creative papers focused on how investments in biosecurity can both contribute to a more equitable society and reduce biological risks. The full prompt is provided below.”
“Winners of the Biosecurity Competition will be awarded the following:
- Online publication of their paper on the NTI website
- The opportunity to attend a high-profile international biosecurity event, such as the Biological Weapons Convention, and present their paper at a prestigious side event.”
Learn more here.
Apply for the 2024 Youth for Biosecurity Fellowship
“The global norm against biological weapons cannot be maintained without youth voices being included in the multilateral discussions taking place in the framework of the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC). Youth perspectives are key to create innovative solutions and generate long-term engagement. There are particular benefits to including the perspectives of young people from developing countries, where most of the world’s youth is concentrated.”
“Organized by the United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs in Geneva in partnership with key international actors empowering youth in science diplomacy and global biosecurity, the Youth for Biosecurity Fellowship provides a unique learning and networking experience into multilateral discussions taking place in the framework of the Biological Weapons Convention in Geneva.”
“Launched in 2019 as a Biosecurity Diplomacy Workshop, the Youth for Biosecurity Initiative organized its first fellowship in 2023. For the second edition, the fellowship will provide the opportunity for 20 young scientists from the Global South to join an online interactive training programme prior to a field visit during the meeting of the BWC Working Group on the Strengthening of the Convention in Geneva.”
Learn more here.
WHO Launches a Mobile App for Biosafety Risk Assessment
“WHO has launched the Risk Assessment Tool (RAST) for Biosafety and Laboratory Biosecurity, developed to help with laboratory risk assessment. Laboratory workers are reported to be up to 1000 times more vulnerable to infections compared to the general population.”
“RAST is designed to complement the WHO Laboratory biosafety manual’s (LBM4) risk- and evidence-based approach. It reflects the first two steps of the risk assessment framework outlined in the LBM4: gather information and evaluate the risks. The app aims to increase understanding of hazards and risks, and to promote thorough assessment and adherence to biological safety practices for laboratory staff.”
Learn more here.



 CDC Lab Closure Due to Safety Concerns
CDC Lab Closure Due to Safety Concerns Financing Pandemic Preparedness At the National Level = First Line of Defense
Financing Pandemic Preparedness At the National Level = First Line of Defense
 NSABB Meeting on DURC and Other Hot Topics
NSABB Meeting on DURC and Other Hot Topics




