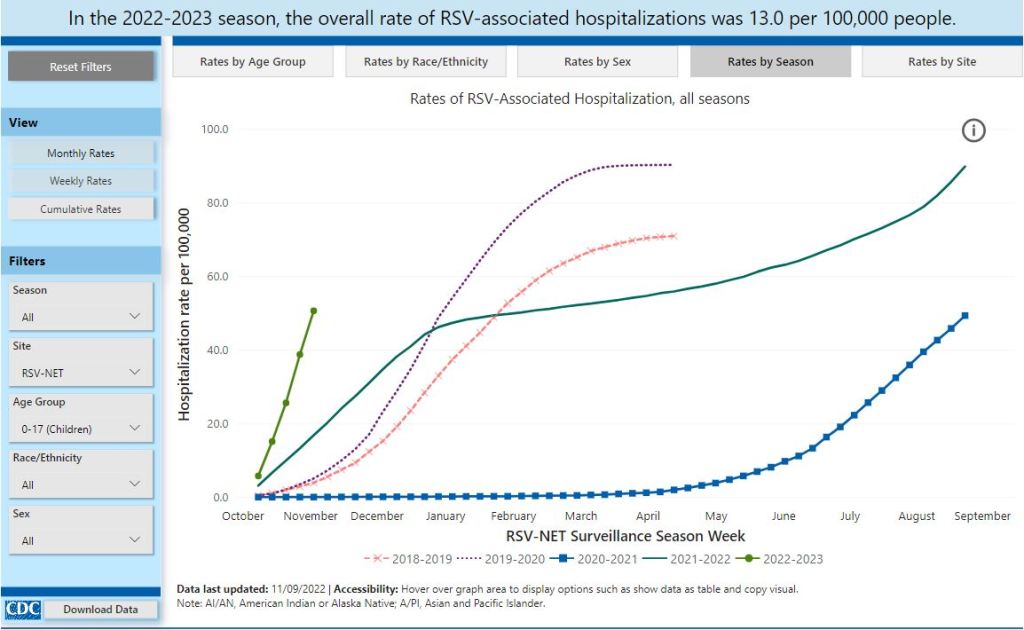
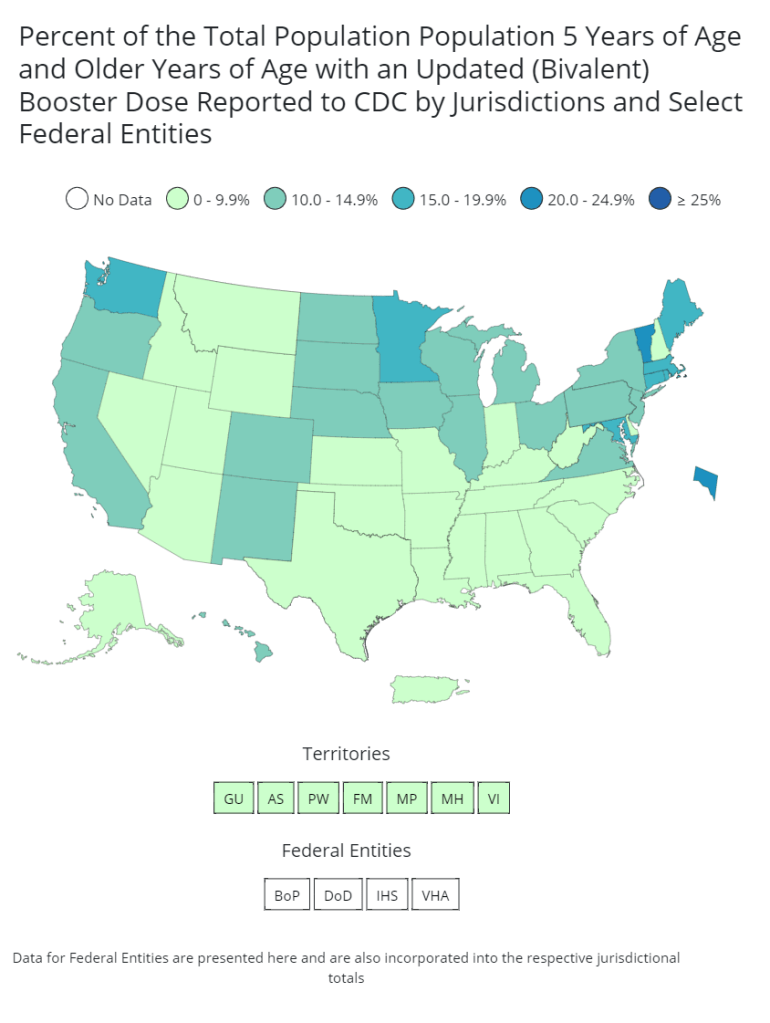
This week’s edition of the Pandora Report covers updates on avian influenza, a recent interim Congressional report on the NIH’s handling of mpox research, a recent report alleging the Department of Defense created an anti-vax misinformation campaign aimed at undermining China’s vaccine diplomacy in the Philippines, and more.
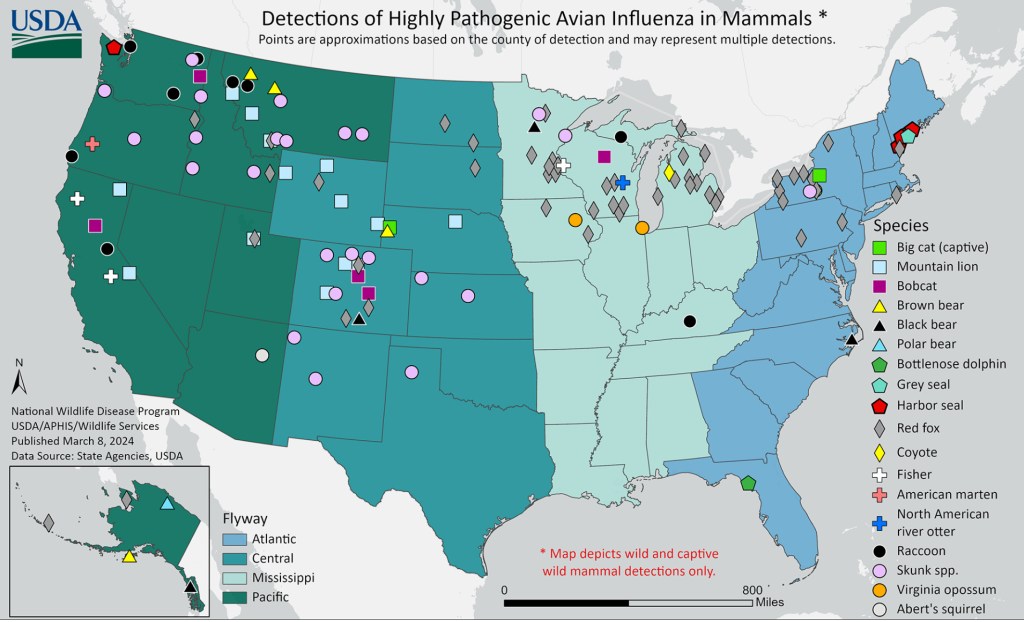
Avian Influenza Updates
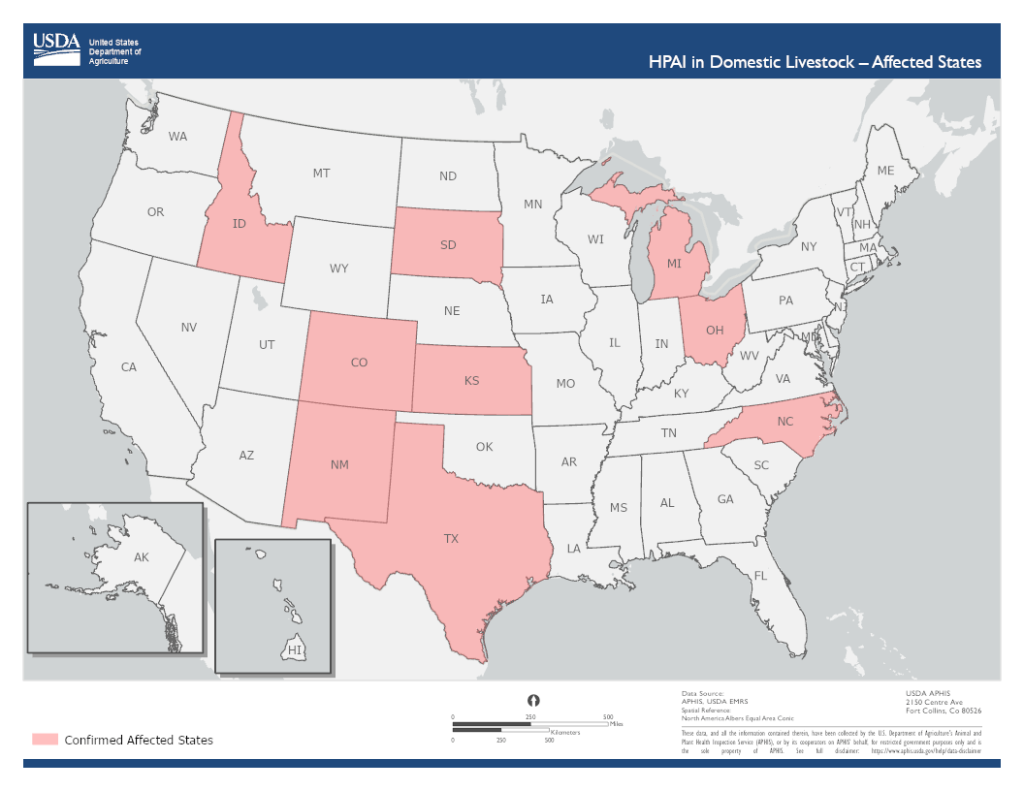
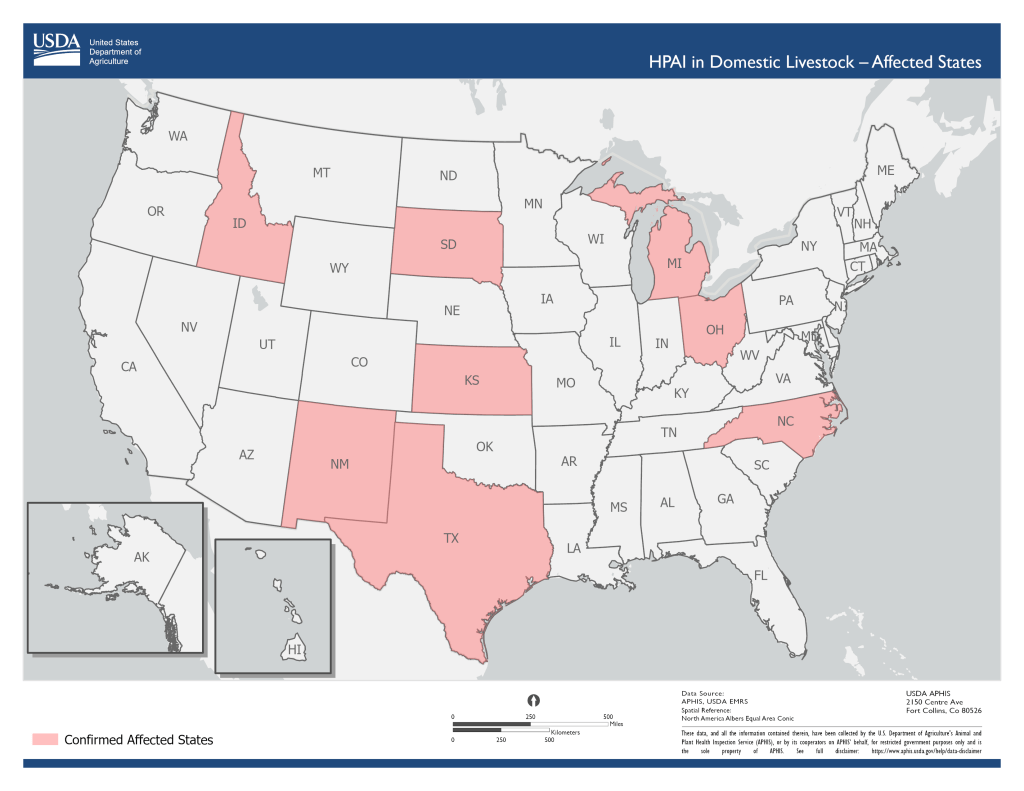
USDA: Twenty-Four Companies Are Working to Create Avian Flu Vaccine for Cattle
Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack told Reuters this week that twenty-four companies are currently working to develop an avian flu vaccine for cattle among continued spread among US dairy herds. Furthermore, Vilsack explained that the USDA is also conducting its own preliminary vaccine research at its laboratory in Ames, Iowa. In addition to looking for a vaccine candidate to test for efficacy, the Department is also researching potential respiratory spread of the virus between cows and working to provide support to farmers to improve biosecurity in their facilities.
Vilsack also promised that a pilot program for bulk milk testing will be rolled out “in the very near future.” The program will hopefully expand testing for H5N1 while enabling healthy herds to move across state lines without needing negative tests from every animal. Vilsack says Michigan and Idaho are among the states that have expressed interest in the program.
First Fatal Human Case of H5N2 Confirmed in Mexico
The WHO confirmed last week that a 59-year-old Mexican man died in April a week after developing fever, shortness of breath, and diarrhea. The Mexican Ministry of Health reports that the man had several comorbidities, including chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, and long-standing systemic arterial hypertension. While the National Institute of Respiratory Diseases in Ciudad de México initially said they found a non-subtypeable influenza A virus in respiratory samples from the patient, the Mexico National Influenza Centre confirmed on May 22 that its subtype was H5N2. While Mexico did report an H5N2 outbreak on a backyard poultry farm in the state bordering the man’s state (Michoacan), it is not yet clear how he contracted the virus.
While this case is unrelated to the ongoing spread of H5N1 in the United States, this is the first case of H5N2 confirmed in a human. Furthermore, H5N2 was the primary culprit in a wave of US outbreaks on poultry farms in the mid-2010s. This was just one decade after an outbreak in Texas in 2004 in a chicken flock in Texas marked the first time in two decades that a dangerous-to-poultry avian flu appeared in the United States.
“Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 Genotype B3.13 in Dairy Cattle: National Epidemiologic Brief”
The USDA recently published this national epidemiologic brief: “On March 25, 2024, USDA announced unpasteurized, clinical samples of milk from sick cattle collected from two dairy farms in Kansas and one in Texas, as well as an oropharyngeal swab from another dairy in Texas, have tested positive for highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI). USDA’s National Veterinary Services Laboratories confirmed the detection as HPAI H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b, genotype B3.13. Phylogenetic analysis and epidemiology support a single introduction into this novel host followed by onward transmission.”
“This report provides field epidemiologic summaries using data collected from epidemiologic questionnaires for H5N1 affected dairy herds.”
Further Reading
CDC: “CDC Reports A(H5N1) Ferret Study Results”
Amy Maxmen and Arthur Allen: “Bird Flu Tests Are Hard To Get. So How Will We Know When To Sound the Pandemic Alarm?” KFF Health News
Samuel V. Scarpino: “Timeline: H5N1 Bird Flu Outbreak in the U.S.,” Think Global Health
Maggie Fox: “H5N1 Bird Flu Isn’t a Human Pandemic–Yet. American Contrariness Could Turn It into One,” Scientific American
Helen Branswell: “In Dribs and Drabs, USDA Reports Suggest Containing Bird Flu Outbreak in Dairy Cows Will Be Challenging,” STAT
BlueDot: ILI Pulse: A(H5N1) Outbreaks in the USA
Katherine J. Wu: “How Much Worse Would a Bird-Flu Pandemic Be?” The Atlantic
Brenda Goodman: “Bird Flu is Rampant in Animals. Humans Ignore it at Our Own Peril,” CNN
Congressional Republicans Target NIH Mpox Research in New Report
Republicans on the House Energy and Commerce Committee released this week a report titled “Interim Staff Report on Investigation into Risky MPXV Experiment at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.” In it, members accuse the NIH of obstructing the investigation of proposed research on MPXV at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), in addition to failing to properly regulate this controversial work. The report explains that, “The primary conclusion drawn at this point in the investigation is that NIAID cannot be trusted to oversee its own research of pathogens responsibly. It cannot be trusted to determine whether an experiment on a potential pandemic pathogen or enhanced potential pandemic pathogen poses unacceptable biosafety risk or a serious public health threat. Lastly, NIAID cannot be trusted to honestly communicate with Congress and the public about controversial GOFROC experiments.”
Science reports that “A spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), NIH’s parent agency, dismissed the report’s conclusions. “The committee is looking for an issue where there isn’t one. HHS and its divisions, including NIH, follow strict biosafety measures as our scientists work to better understand and protect the public from infectious diseases—like mpox,” the spokesperson said.”
The investigation is one of many Congressional efforts to probe concerns about biosafety in laboratories and other concerns raised by the pandemic. This investigation was launched in late 2022 after Bernard Moss, a well-known poxvirus researcher at NIAID, described research he was planning to conduct in a Science news article.
Science explains that “Moss was trying to understand the difference between the virulent clade I monkeypox virus strain causing outbreaks mostly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the milder clade II virus, which spread from West Africa around the world in 2022. In a first effort, Moss said he had inserted genes from milder clade II into a clade I virus, without seeing it become less dangerous in mice. He told Science he was next planning to explore the reverse transfer: whether inserting genes from clade I into clade II viruses made these usually milder viruses more lethal to mice.”
“Some researchers raised the alarm, worried the study qualified as risky GOF research because the resulting virus could be much more dangerous and even touch off a pandemic. Committee members say that when they sought more information from NIH and NIAID on the experiments, they were initially told the transfer of genes from clade I to clade II was never approved…Then in March, NIAID revealed that its biosafety committee had signed off on a project that included such gene transfers in 2015, but that researchers never followed through; they only moved genes from clade II to clade I. The HHS spokesperson says, “The experiment referenced by the committee was never conducted, which the committee knows.”’

The Committee’s press release explains that “For nearly a year and a half, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the NIH, and NIAID misrepresented and deceived the Committee by repeatedly denying that the potentially dangerous experiment was proposed and approved. However, after being pressed repeatedly by Committee Leaders, HHS ultimately admitted Dr. Moss’s research team had been granted approval to conduct a bidirectional MPVX gene-transfer experiment (i.e., inserting the more lethal strain into the more transmissible strain and vice versa). Documents made available for review to Committee staff confirmed the 2015 approval of the experiment and raised additional concerns.”
It continues with “HHS, the NIH, and NIAID still maintain the riskier research project was never conducted. However, no documentation or any other evidence has been produced to substantiate the claim. NIAID has also failed to offer any explanation of the circumstances and rationale that supposedly led the Moss research team to drop the bidirectional mpox gene-transfer experiment after receiving approval for the project. “
The report also raises concerns about existing federal rules covering gain-of-function research, suggesting that they currently do not do enough because they allow researchers, their institutions, and NIAID to decide which projects fit the definition of GOF work. The report argues this is an “inescapable conflict of interest,” and that screening should be conducted by a panel at HHS or a new “wholly independent” entity.
The Committee also expressed disagreement with how GOF is defined in the new federal rules and made several more conclusions, including “NIAID has a culture of secrecy and obfuscation regarding experiments involving pandemic and potential pandemic pathogens. HHS and the NIH are complicit in enabling NIAID’s culture of secrecy and obfuscation. This is incompatible with accountable, democratic governance and further erodes the public’s trust in government health agencies,” and “: Principal investigators, research institutes, and funding agencies are poorly positioned to, and perhaps incapable of, conducting adequate risk/benefit analysis and oversight of experiments that—by virtue of having proposed them and approved their funding—they want to see conducted. This is an inescapable conflict of interest and misalignment of incentives that results in experiments being approved and conducted without sufficient scrutiny or ongoing oversight.”
Report Alleges US Department of Defense Ran “Secret Anti-Vax Campaign to Undermine China During Pandemic”
A recent report from Reuters claims that, “At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. military launched a secret campaign to counter what it perceived as China’s growing influence in the Philippines, a nation hit especially hard by the deadly virus.”
The report’s authors, Chris Bing and Joel Schectman, continue, writing “The clandestine operation has not been previously reported. It aimed to sow doubt about the safety and efficacy of vaccines and other life-saving aid that was being supplied by China, a Reuters investigation found. Through phony internet accounts meant to impersonate Filipinos, the military’s propaganda efforts morphed into an anti-vax campaign. Social media posts decried the quality of face masks, test kits and the first vaccine that would become available in the Philippines – China’s Sinovac inoculation.”
The report later explains that “The U.S. military’s anti-vax effort began in the spring of 2020 and expanded beyond Southeast Asia before it was terminated in mid-2021, Reuters determined. Tailoring the propaganda campaign to local audiences across Central Asia and the Middle East, the Pentagon used a combination of fake social media accounts on multiple platforms to spread fear of China’s vaccines among Muslims at a time when the virus was killing tens of thousands of people each day. A key part of the strategy: amplify the disputed contention that, because vaccines sometimes contain pork gelatin, China’s shots could be considered forbidden under Islamic law.”
“The military program started under former President Donald Trump and continued months into Joe Biden’s presidency, Reuters found – even after alarmed social media executives warned the new administration that the Pentagon had been trafficking in COVID misinformation. The Biden White House issued an edict in spring 2021 banning the anti-vax effort, which also disparaged vaccines produced by other rivals, and the Pentagon initiated an internal review, Reuters found.”
Read more here.
OPCW Fact-Finding Mission Concludes Latest Investigations into Reports in Syria
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons recently announced its Fact-Finding Mission (FFM) in Syria concluded “…that the information obtained and analysed is not sufficient to provide reasonable grounds to determine that toxic chemicals were used as a weapon in the reported incidents that occurred on 9 August 2017 in Qalib al-Thawr and 8 November 2017 al-Balil, Hama Governorate, the Syrian Arab Republic.”
Read more about the FFM, these two reports from the Syrian Arab Republic, and the FFM’s conclusions here.

“Russia Spreads Disinformation to Cover Up Its Use of Chemical Weapons in Ukraine”
The Department of State’s Global Engagement Center recently published this report in several languages discussing Russia’s use of chemical weapons and its efforts to conceal that use in Ukraine. It explains in part, “Russia’s use of such chemicals is not an isolated incident, and is probably driven by Russian forces’ desire to dislodge Ukrainian forces from fortified positions and drive them into the line of fire, the exact reason the CWC prohibits the use of RCA as method of warfare, and achieve tactical gains on the battlefield. Russia retains an undeclared chemical weapons program and has used chemical weapons, such as the Novichok nerve agents, at least twice in recent years in assassination attempts.”
“Catalyzing Crisis: A Primer on Artificial Intelligence, Catastrophes, and National Security”
Bill Drexel and Caleb Withers authored this report for CNAS: “The arrival of ChatGPT in November 2022 initiated both great excitement and fear around the world about the potential and risks of artificial intelligence (AI). In response, several AI labs, national governments, and international bodies have launched new research and policy efforts to mitigate large-scale AI risks. However, growing efforts to mitigate these risks have also produced a divisive and often confusing debate about how to define, distinguish, and prioritize severe AI hazards. This categorical confusion could complicate policymakers’ efforts to discern the unique features and national security implications of the threats AI poses—and hinder efforts to address them. Specifically, emerging catastrophic risks with weighty national security implications are often overlooked between the two dominant discussions about AI concern in public discourse: present-day systemic harms from AI related to bias and discrimination on the one hand, and cantankerous, future-oriented debates about existential risks from AI on the other.”
“This report aims to: Demonstrate the growing importance of mitigating AI’s catastrophic risks for national security practitioners, Clarify what AI’s catastrophic risks are (and are not), Introduce the dimensions of AI safety that will most shape catastrophic risks.”
“Driving AIxBio Innovation Through Data and Standardization”
The National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology recently published this paper: “If the United States wants to remain a leader in artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology (AIxBio), it must treat biological data as a strategic asset to support the next phase of AIxBio models. These models will rely on biological data sets of unprecedented scale, likely generated through high-throughput lab automation and new experimental methods. Biological data enable the use of AIxBio models, but advances in AIxBio are limited by the availability of appropriate and usable data.1 Additionally, data standardization would enable the United States to combine data from across its robust and diverse life science ecosystem to further advance AIxBio and maximize its potential benefits. This white paper describes considerations for generating and standardizing biological data to support continued AIxBio research, development, and application.”
“APP3 Statement on the Importance of Biosafety and Biosecurity in the Age of Artificial Intelligence and Emerging Technologies”
This statement was recently released by the GHSA Action Package Prevent-3 on Biosafety and Biosecurity, Emerging Biological Risks Working Group: “As advances in AI and emerging technologies continue to increase worldwide quickly, there are growing concerns that AI tools and other emerging technologies could act synergistically with synthetic biotechnologies to cause significant harm. The APP3 believes it is imperative to understand further and mitigate the biological risks of AI and emerging biotechnologies, reduce the risk of technology misuse, and protect economic and global health security. Efforts to raise awareness within the GHSA community, cultivate responsible scientific work, strengthen biosecurity controls, and mitigate biological risks associated with new technologies globally are critical.”
Read more here.
“Why the Global Bioeconomy Urgently Needs Technical Standards and Metrics”
Paul Freemont, India Hook-Barnard, and Matthew Chang published this piece with the World Economic Forum, in which they write “The global bioeconomy is estimated to be worth about $4 trillion, and more than 50 nations now have published bioeconomy strategies or have policies steering towards a sustainable bioeconomy. With the development of new technologies in engineering and synthetic biology, the bioeconomy is growing rapidly…Growth of the sector will bring increased commercialization, scale-up and distributed manufacturing, and promote manufacturing resilience by diversifying production streams beyond traditional chemical manufacturing.”
“However, the current lack of standards and metrics that apply directly to such a large global industry could result in chaos, with failed interoperability and an inability to share data or allow for technology transfer internationally…The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has published only 35 standards directly related to biotechnology; in comparison, there are 79 published standards relating specifically to dental instruments…As such, there is a call from industry representatives and academics alike to develop technical standards and metrics that can be applied across the innovation pipeline to support the growth of the bioeconomy.”
“The Viral Most Wanted: The Orthomyxoviruses”
Kate Kelland continues CEPI’s “The Viral Most Wanted” with this latest installment: “It’s considered the most deadly single contagious disease event in all of human history and infected 500 million people worldwide—a third of the planet’s population.”
“It struck in three merciless waves—the first, relatively mild, in March 1918; the second, more brutal, in August 1918; and the third and deadliest of all in late 1918, running through the first few months of 1919.”
“It is estimated to have killed almost five times as many people as were killed during World War One.”
“More than half of the people it killed were fit, strong, healthy young adults in the prime of life—including millions of World War One soldiers.”
“Its victims often died within hours or days of developing symptoms. Their skin would turn blue and their lungs would fill with fluid, causing them to suffocate from within.”
“This was the Spanish Flu—the Great Influenza pandemic of 1918-1919—caused by a virus called influenza type A subtype H1N1. It and its many life-threatening relatives are part of the Orthomyxovirus family—one of The Viral Most Wanted.”
“Countering Disinformation and Misinformation in Animal Health Emergencies”
The World Organisation for Animal Health and INTERPOL recently released this set of guidelines: “To orient Veterinary Services, Aquatic Animal Health Services and Law Enforcement to these issues and introduce some key strategies to manage disinformation and misinformation, these guidelines have been prepared by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the International Criminal Police Organisation (INTERPOL). They draw from a June 2022 virtual workshop convened as part of the WOAH, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and INTERPOL Project on ‘building resilience against agro-crime and agro-terrorism’, which was funded by Global Affairs Canada’s Weapons Threat Reduction Program [1].”
“The guidelines provide a starting point for these services and agencies, as well as organisations working in animal health emergencies, to prepare for, detect and respond to disinformation and misinformation. Since this is a fast-moving area with much information and guidance already available, this document includes links to further resources that offer more detail on specific strategies and actions.”
“WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance”
From WHO: “The 2024 WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List (WHO BPPL) is an important tool in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance. Building on the 2017 edition, the 2024 WHO BPPL updates and refines the prioritization of antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens to address the evolving challenges of antibiotic resistance. The list categorizes these pathogens into critical, high, and medium priority groups to inform research and development (R&D) and public health interventions.”
“The 2024 WHO BPPL covers 24 pathogens, spanning 15 families of antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens. Notable among these are Gram-negative bacteria resistant to last-resort antibiotics, drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis, and other high-burden resistant pathogens such as Salmonella, Shigella, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. The inclusion of these pathogens in the list underscores their global impact in terms of burden, as well as issues related to transmissibility, treatability, and prevention options. It also reflects the R&D pipeline of new treatments and emerging resistance trends.”
“The WHO BPPL acts as a guide for prioritizing R&D and investments in AMR, emphasizing the need for regionally tailored strategies to effectively combat resistance. It targets developers of antibacterial medicines, academic and public research institutions, research funders, and public–private partnerships investing in AMR R&D, as well as policy-makers responsible for developing and implementing AMR policies and programs.”
“Further details on the rationale behind the list, the methodologies used to develop the list and the key findings, can be found in the accompanying report.”
“A Long COVID Definition: A Chronic, Systemic Disease State with Profound Consequences”
From NASEM: “The lack of a clear and consistent definition for Long COVID presents challenges for policymakers, researchers, public health professionals, clinicians, support services, and patients. As such, the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response and the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health asked the National Academies to assemble a committee of experts to produce a consensus definition for Long COVID. The resulting report, A Long COVID Definition: A Chronic, Systemic Disease State with Profound Consequences, presents the 2024 NASEM Long COVID Definition, developed based on findings reported in existing literature, as well as stakeholder and patient input.”
Read here.
“Pentagon Playing Catch Up After Years Neglecting Nuclear Protection”
Stew Magnuson recently published this piece in National Defense discussing the Army’s recent report, “An Independent Assessment of the Army’s Ability to Fight and Win on a Nuclear Battlefield.” He writes in part, “The Army Science Board in September completed work on a report, “An Independent Assessment of the Army’s Ability to Fight and Win on a Nuclear Battlefield.”
“Its conclusions were not revealed to the public and are available to read only on classified networks. But listening to a handful of government experts at a recent presentation who did have access to the report, its overall conclusions must be alarming.”
What We’re Listening to 🎧
Voices from DARPA Podcast Episode 79: Integrating ELSI
“In this episode, we’ll be taking a deeper dive into ELSI – ethical, legal, and societal implications of new technologies and capabilities – and specific examples of how DARPA programs have incorporated those considerations into their structure.”
“We’re highlighting three examples of how DARPA integrated ELSI throughout the program lifecycle via the counsel of experts from the medical, scientific, legal, and ethics communities to assist program managers and performers in identifying and mitigating any potential issues.”
“The first program, out of our Biological Technologies Office, is Safe Genes, which supported force protection and military health and readiness by developing tools and methodologies to control, counter, and even reverse the effects of genome editing—including gene drives—in biological systems across scales.”
“The second program, Urban Reconnaissance through Supervised Autonomy (URSA) from our Tactical Technology Office (TTO) aimed to enable improved techniques for rapidly discriminating hostile intent and filtering out threats in complex urban environments.”
“And, finally, the current In the Moment program in our Information Innovation Office (I2O) seeks to identify key attributes underlying trusted human decision-making in dynamic settings and computationally representing those attributes, to generate a quantitative alignment framework for a trusted human decision-maker and an algorithm.”
Listen here.
NEW: Upcoming Hearing on COVID-19 Origins
“Biodefense Program Director, Dr. Gregory Koblentz, will be testifying at the upcoming Senate Homeland Security and Government Affairs hearing on “Origins of COVID-19: An Examination of Available Evidence,” which will be held on Tuesday, June 19 at 10 AM. Also testifying will be Dr. Robert Garry from Tulane University, Dr. Stephen C. Quay from Atossa Therapeutics, and Dr. Richard H. Ebright from Rutgers University.”
NEW: Why Isn’t the World Ready for the Next Pandemic? How Can It Be?
From the Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response: “The Right Honourable Helen Clark and Her Excellency Ellen Johnson Sirleaf explore these questions and provide answers in their new report: No Time to Gamble: Leaders Must Unite to Prevent Pandemics.”
This virtual event will take place on June 18 at 1 pm CET. Learn more and register here.
NEW: IRF Book Launch: Essentials of Biological Security: A Global Perspective
The Interdisciplinary Research Forum is hosting this book launch for Essentials of Biological Security: A Global Perspective by Lijun Shang, Weiwen Zhang, and Malcolm Dando: “Improving biosecurity education appears to be a key means to address the need for awareness raising and education about the dangers of the dual use research for life scientists within a culture of responsible research under BTWC or CBW. Although it has been advocated for a long time, it still presents a challenging task for all stakeholders, especially for life science communities.”
“In this launching workshop, the leading editor Professor Lijun Shang will explain the background of initiation of this book, including the purpose and strategy plan of using the book to implement biosecurity education. Professor Malcolm Dando will give an overview of the book with brief introduction of each chapter, and Professor Weiwen Zhang will talk about our promotion plan for this book, including translation, workshops, and future publication plans.”
“We will also have chapter authors to briefly introduce their individual chapters either in person or through a video recording. Finally, we will have Iris Magne to talk about our plans of using this book as a first stepping stone in the current project of Building up An International Security Education Network to include the book.”
This event will take place on June 14 at 2 pm BST. Learn more and register here.
NEW: DARPA B-SAFE Industry Day
From DARPA: “The rapidly evolving field of advanced genome editing tools has enabled the ability to modify genetic material in a manner that is precise, rapid, cost-effective, and broadly accessible. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-associated protein (Cas) or CRISPR-Cas technologies represent one of the most widely adopted tools in the genome engineering toolkit, and its advancement has revolutionized the field of biotechnology and genetic engineering. However, concerns regarding the precision, specificity, and control of CRISPR-Cas systems remain. The DARPA Broad-Spectrum Antagonists For Editors, or B-SAFE, program aims to develop platform technologies for highly potent inhibitors for multiple classes, types, and species of editors with enhanced activity, utility, and breadth of coverage. The B-SAFE program will also address the challenge of inhibitor molecules keeping pace with the discovery of novel editing systems by developing a platform for rapid discovery and development of inhibitors of novel, emergent gene editor technologies. The B-SAFE program will produce tools capable of complete inhibition of CRISPR-Cas systems with minimal off-target effects. Platforms must be capable of inhibiting DNA editors (Cas9 and Cas12 species) but approaches that also include RNA editors, other DNA editors, and emerging technologies are encouraged. The ideal solution would be capable of inhibiting all Cas9 and Cas12 species.”
This event will take place virtually and in-person on June 28. Learn more and register here.
The Advancing Threat Agnostic Biodefense Webinar Series-Computational and Systems Biology Advances to Enable Bioagent Agnostic Signatures
From PNNL: “Join us as we welcome Andy Lin, Computational Biologist at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. His talk, titled “Computational and Systems Biology Advances to Enable Bioagent Agnostic Signatures” will be Tuesday, June 18, at noon PT.”
“Enumerated threat agent lists have long driven biodefense priorities. The global SARS-CoV-2 pandemic demonstrated the limitations of searching for known threat agents as compared to a more agnostic approach. Recent technological advances are enabling agent-agnostic biodefense, especially through the integration of multi-modal observations of host-pathogen interactions directed by a human immunological model.”
“Although well-developed technical assays exist for many aspects of human-pathogen interaction, the analytic methods and pipelines to combine and holistically interpret the results of such assays are immature and require further investments to exploit new technologies.”
“In this talk, we discuss potential immunologically based bioagent-agnostic approaches and the computational tool gaps the community should prioritize filling.”
Register here.
Registration for GHS 2024 Now Open
Registration is now open for the Global Health Security 2024 conference in Sydney, Australia. This iteration will take place 18-21 June, 2024. The call for abstracts is also still open. “The mission of the Global Health Security conference is to provide a forum where leaders, researchers, policy-makers, and representatives from government, international organisations, civil society, and private industry from around the world can engage with each other, review the latest research and policy innovations, and agree solutions for making the world safer and healthier. To that end, our mission is to help foster a genuinely multidisciplinary community of practice that is committed to working collaboratively to enhance global health security and eliminate disease, irrespective of its origin or source.”
SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology, and Biosecurity Conference in Africa
“Join us for the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa, a groundbreaking event that brings together experts, researchers, and enthusiasts in the field of synthetic biology. This in-person conference will take place at the Laico Regency Hotel from Wed, Jul 17, 2024 to Friday, Jul 19, 2024.”
“Get ready to dive into the exciting world of synthetic biology and explore its potential applications in Africa. From cutting-edge research to innovative solutions, this conference offers a unique opportunity to learn, network, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.”
“Discover the latest advancements, trends, and challenges in synthetic biology through engaging keynote speeches, interactive workshops, and thought-provoking panel discussions. Immerse yourself in a vibrant atmosphere where ideas flow freely and new connections are made.”
“Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in synthetic biology, this conference provides a platform to expand your knowledge, exchange ideas, and contribute to the growth of the field in Africa.”
“Don’t miss out on this extraordinary event that promises to shape the future of synthetic biology and biosecurity in Africa. Mark your calendars and join us at the SBA.3 International Synthetic Biology and Biosecurity Conference in Africa!”
Learn more and register here.
Jobs Postings: Detailee (Current Federal Employee), Policy Analyst, Policy Advisor
The National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology (NSCEB) currently has multiple job openings for those who are current federal employees or those who already hold a TS clearance with TS/SCI preferred. Learn more and apply here.
Job Posting: Research Associate (Global Health Law & Governance)
The National University of Singapore is currently hiring a research associate focused on global health law and governance: “The Global Health Law and Governance Program at the NUS Centre for international Law is recruiting a one-year Research Associate position. The Program focuses on the international legal, regulatory and governance aspects of pandemic prevention and response, as well as international public health emergencies. Topics of interest include the World Health Organization’s negotiations on a new pandemic accord, the revision of the International Health Regulations, improving fair and equitable access to medicines, access and benefit sharing of pathogen samples/genetic sequencing data, intellectual property and technology transfer, global health innovation and technologies, and more. The program conducts research, offers education and training, and organizes events. The Research Associate will support the work of the Program and will also undertake a personal research project.”
Learn more and apply here.